| R | Fl | A | B | H | L | loc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 693.3 | 50 | 1972 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 422.0 | 54 | 1972 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 736.6 | 70 | 1972 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 732.2 | 50 | 1972 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 1295.1 | 55 | 1893 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 1195.9 | 59 | 1893 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
The R software
Introduction
residualsin GAMLSSan example; the
rent99dataRpackages
Residuals
Introduction
GAMLSS uses as
residualsthenormalised quantile residuals\(\equiv\)z-scores
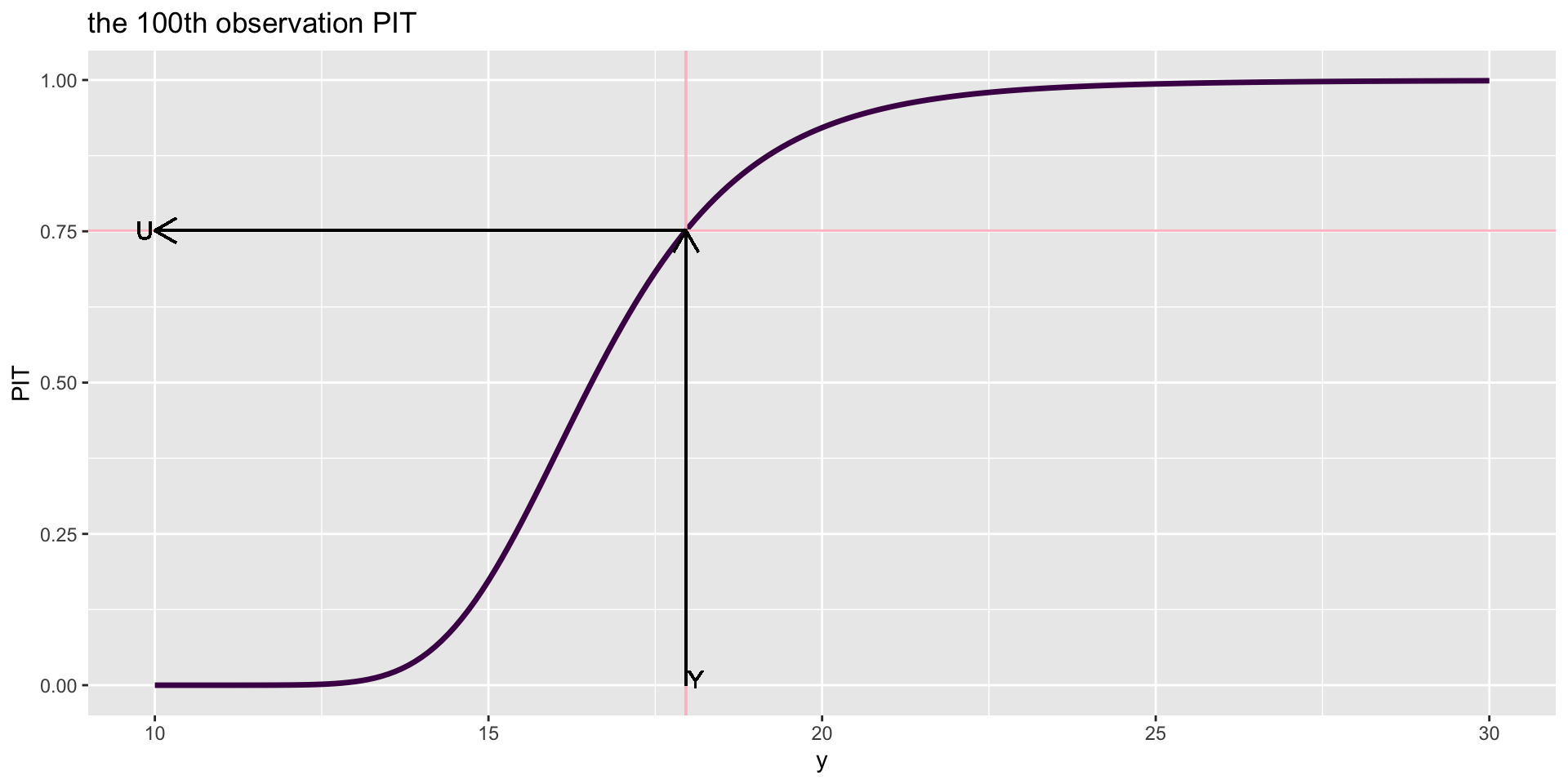
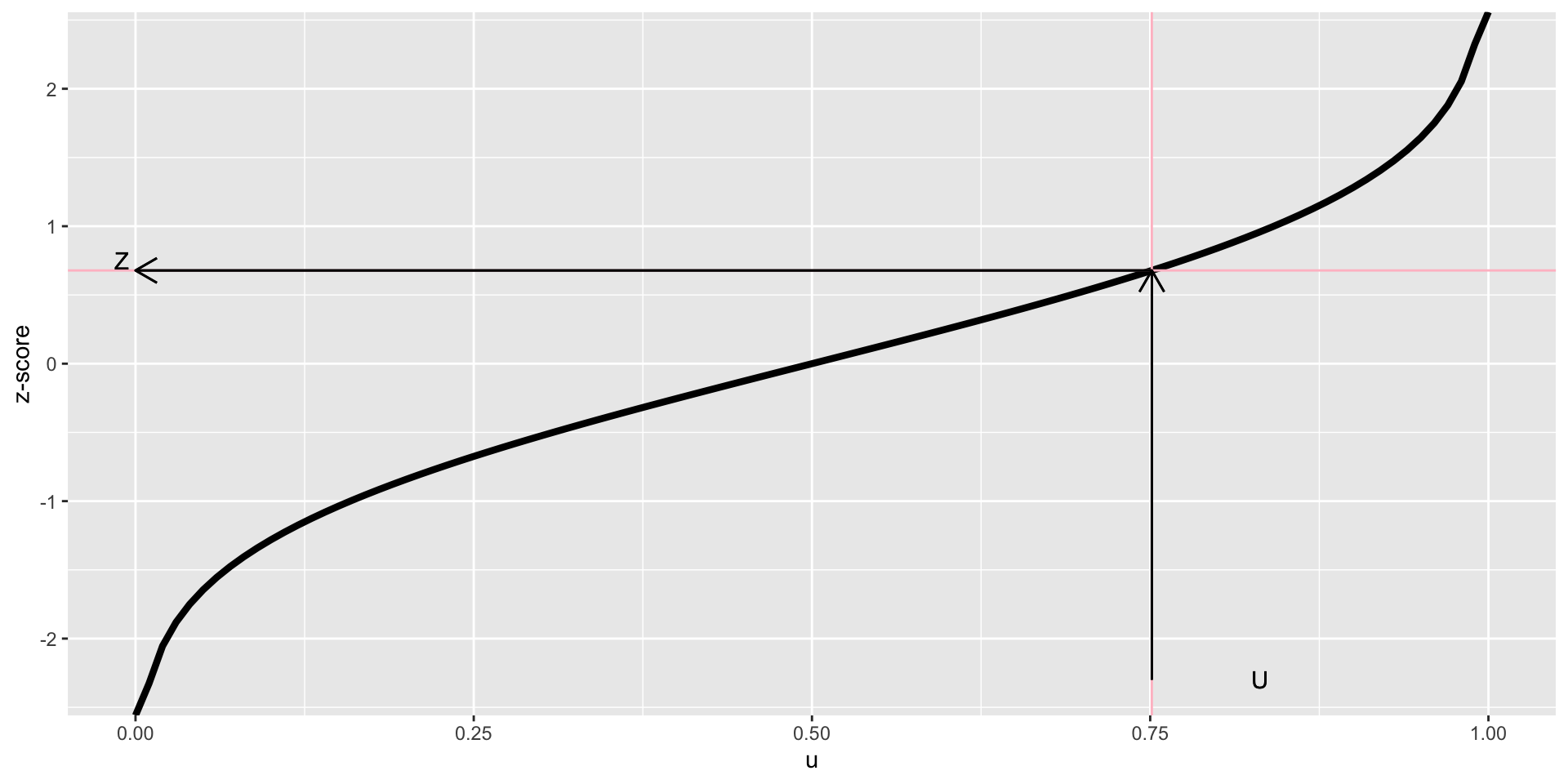
PIT and z-scores residuals
let \(y_i\) and \(F(y_i, \hat(\theta)_i)\) be the ith observation and its fitted cdf respectively. Then the Probability Integral Transformed (PIT) residuals are
\[u_i = F(y_i, \hat(\theta)_i) \] and the z-scores residuals are
\[z_i = \Phi^{-1}(y_i, \hat(\theta)_i) \]
properties
If the distribution of \(y_i\) is specified correctly then PIT are uniform;
i.e \[u_i \sim U(0,1)\]
and z-scores are normally distributed
i.e. \[z_i \sim NO(0,1)\]
PIT
z-scores
diagnostics plots
residuals plots against other variables
index x-variable parameters quantilesqqplots
worm plots
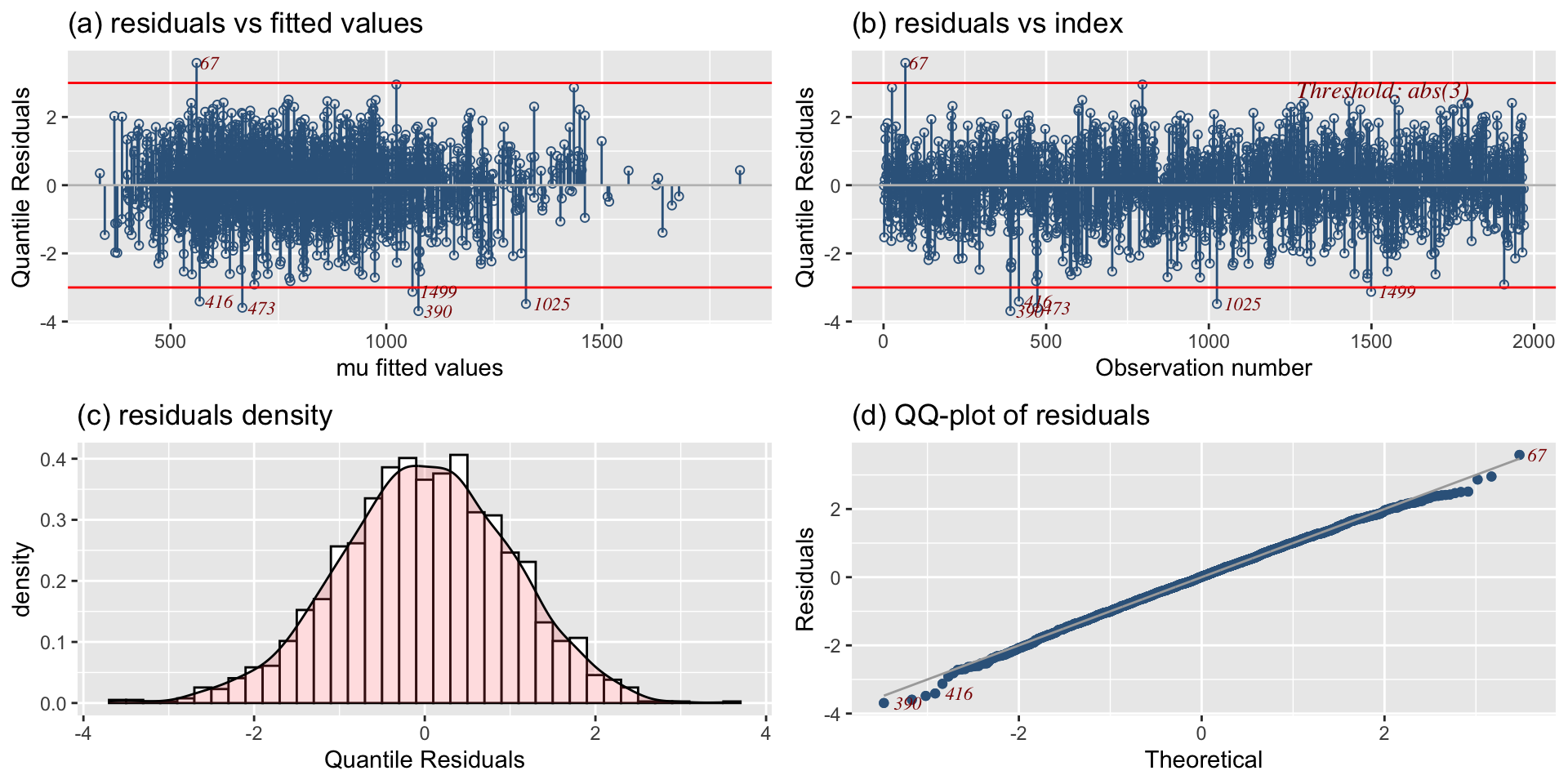
density plots
bucket plots
skewness plots
Example: rent
Data
| obs number | y | x1 | x2 | x3 | … | xr-1 | xr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | y1 | x11 | x12 | x13 | … | x1r-1 | x1r |
| 2 | y2 | x21 | x22 | x23 | … | x2r-1 | x2r |
| 3 | y3 | x31 | x32 | x33 | … | x3r-1 | x3r |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| n-1 | yn-1 | xn-11 | xn-12 | xn-12 | … | xn-1r-1 | xn-1r |
| n | yn | xn1 | xn2 | xn3 | … | xnr-1 | xnr |
The rent 1999 Munich data
Fitting
residual plots agaist index
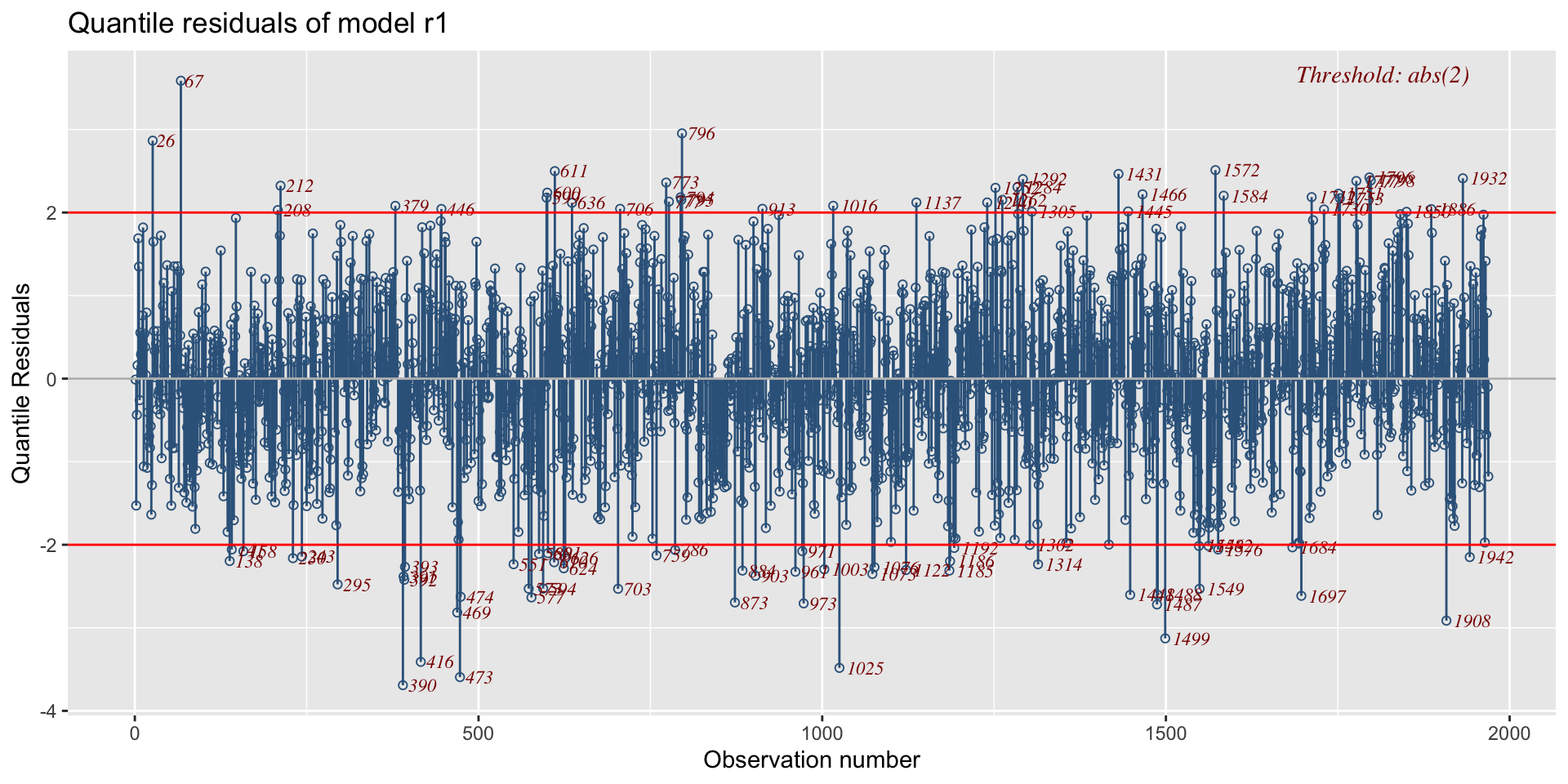
against continuous x-variables
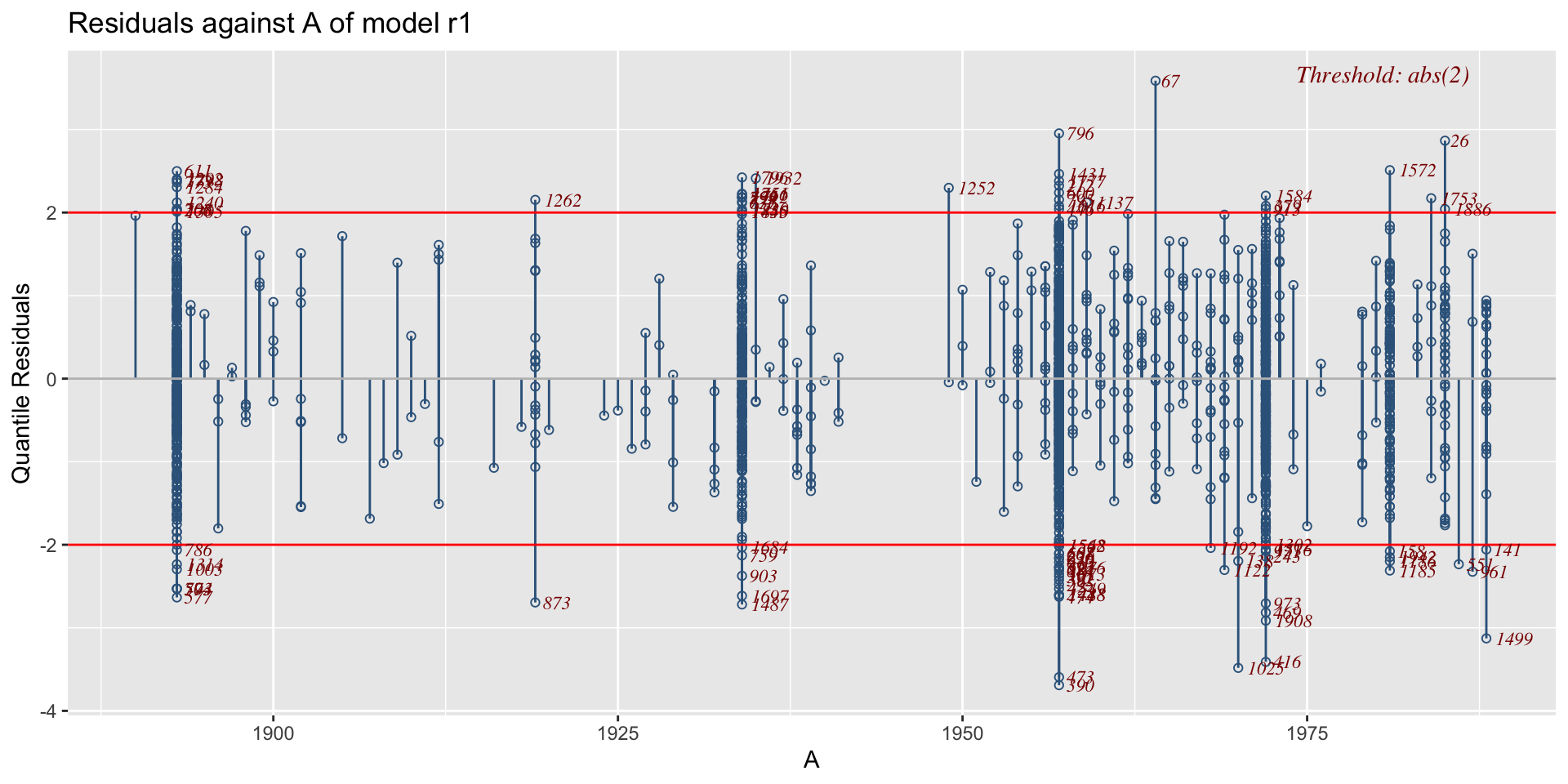
against factor x-variables
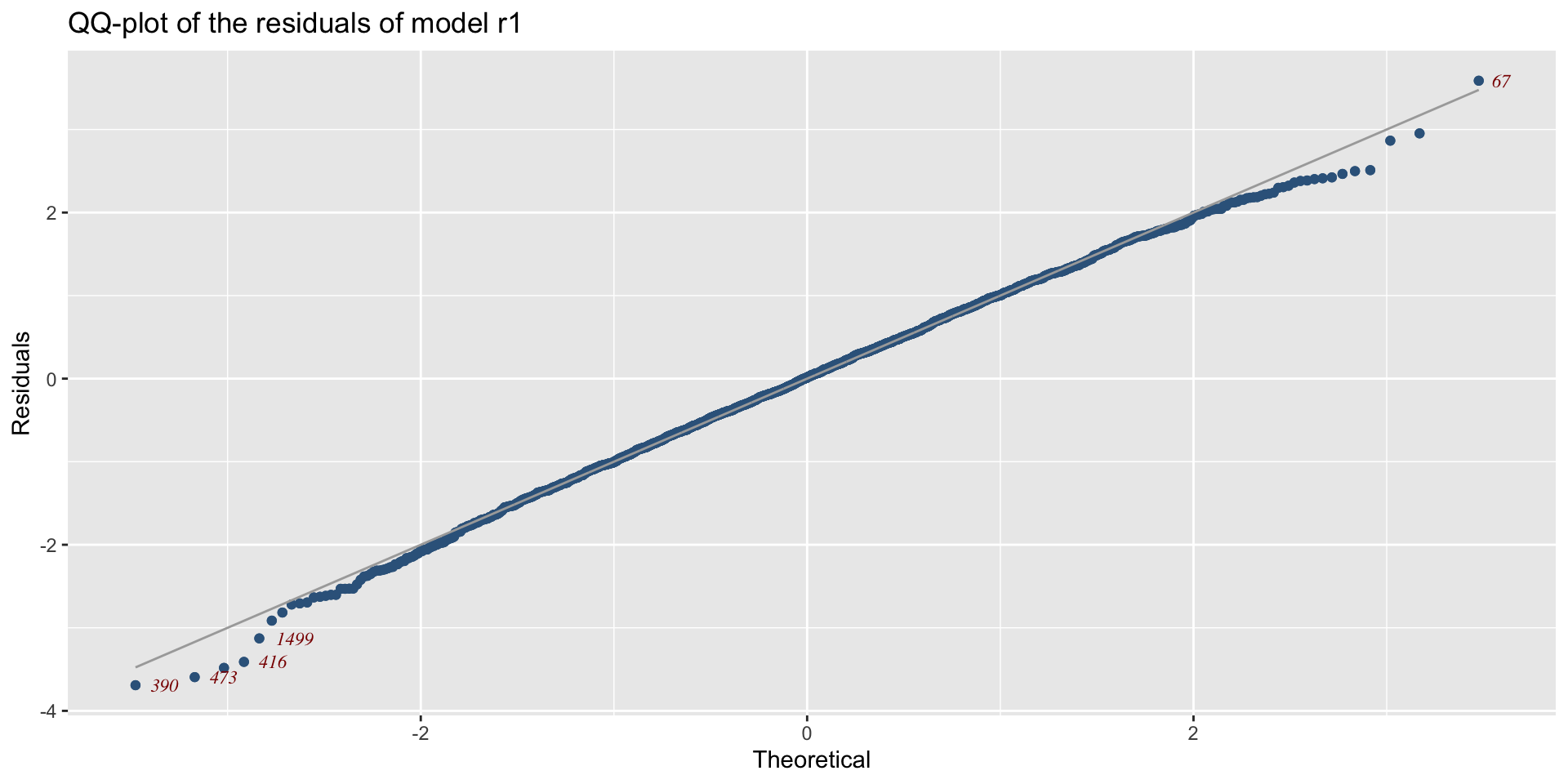
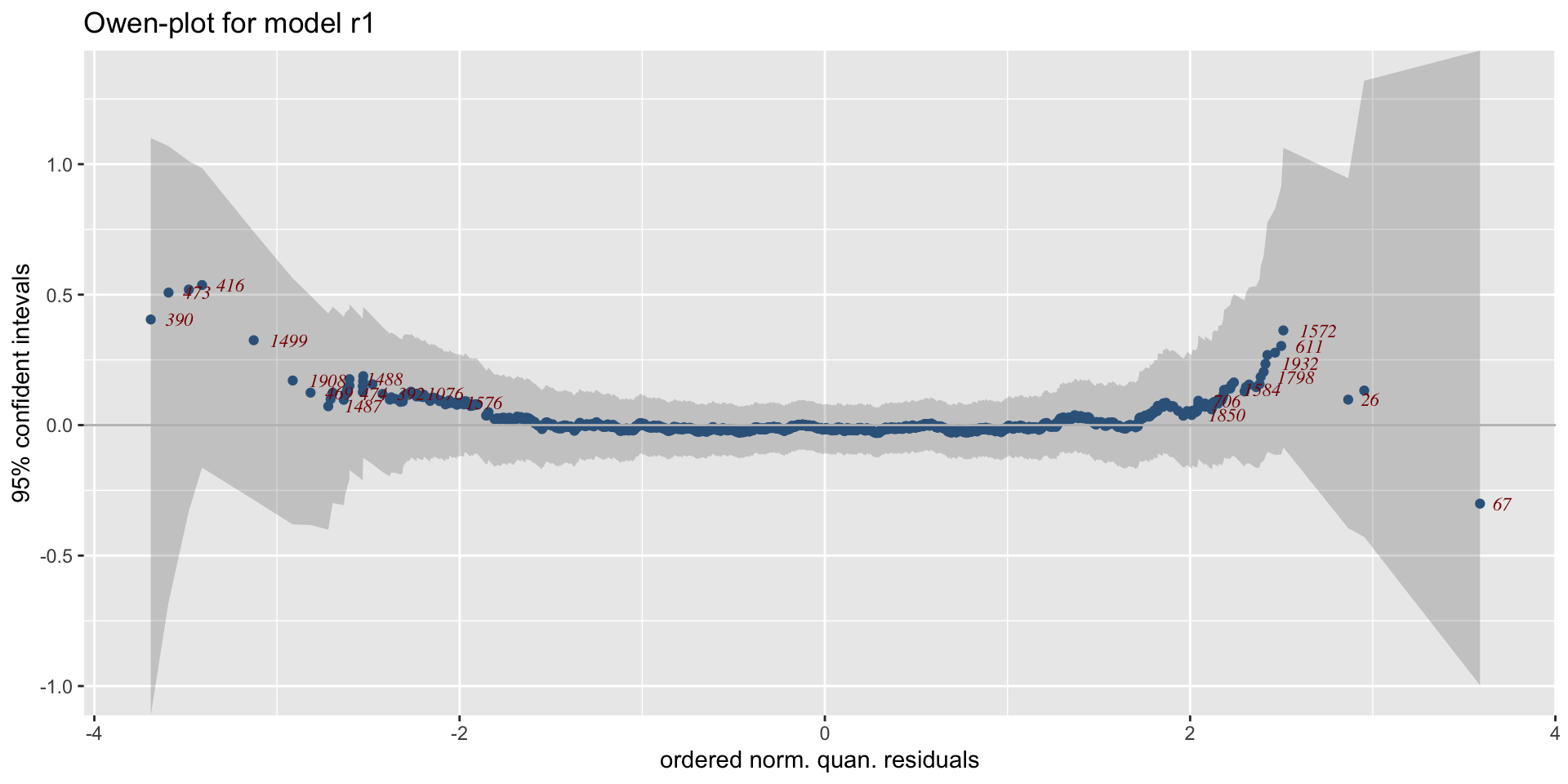
QQ-plots
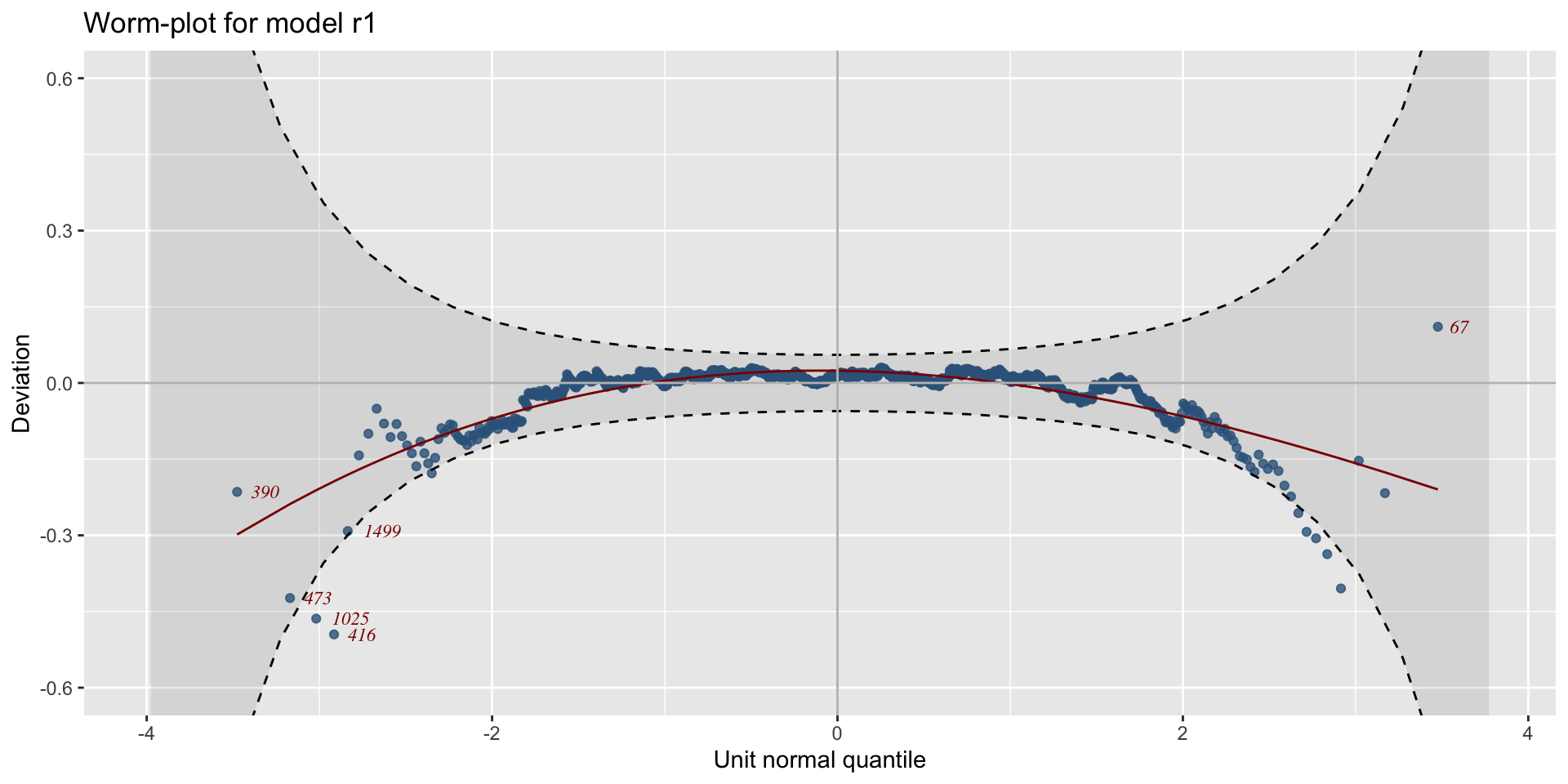
worm plots
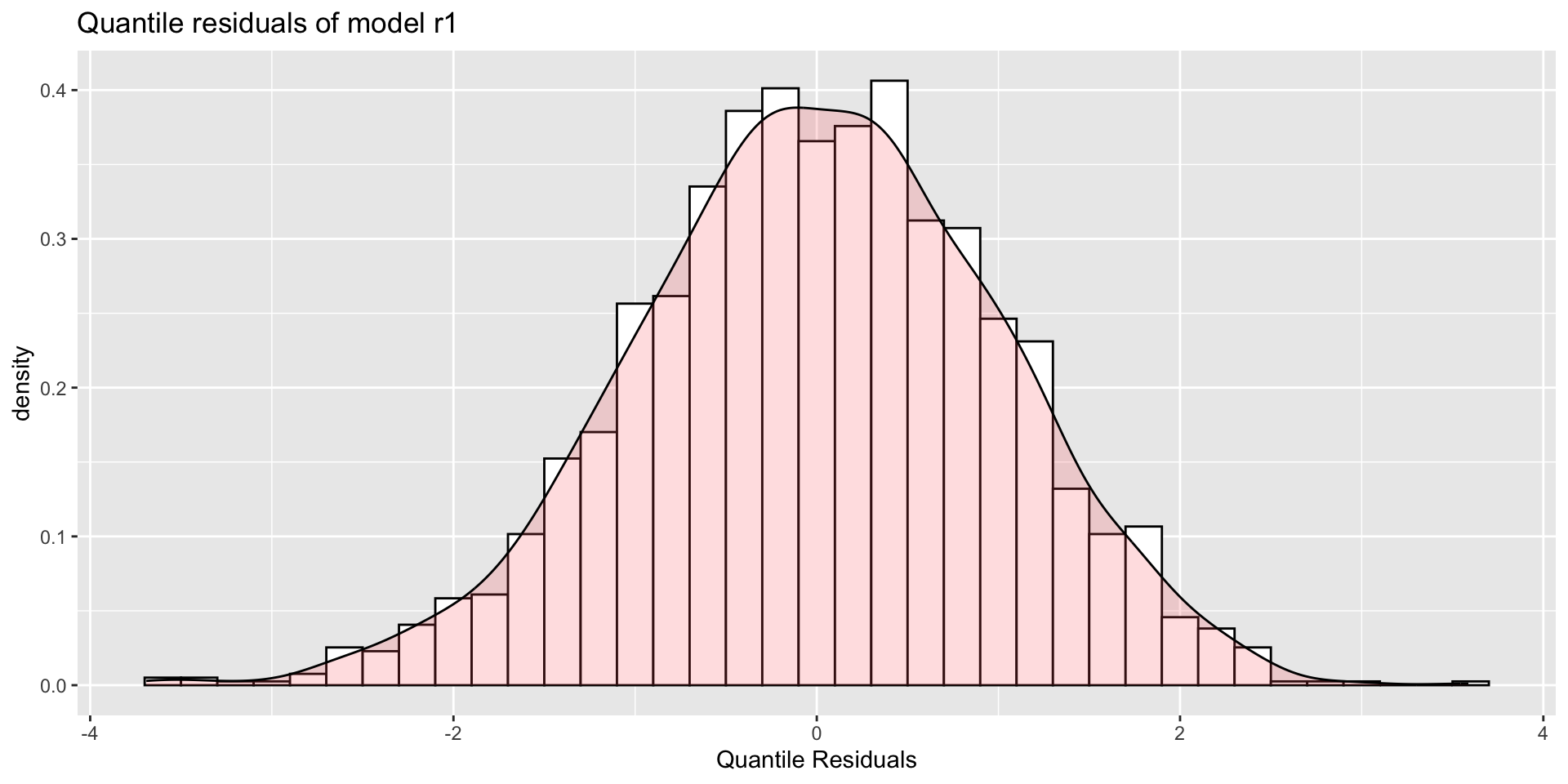
density plots
bucket plots
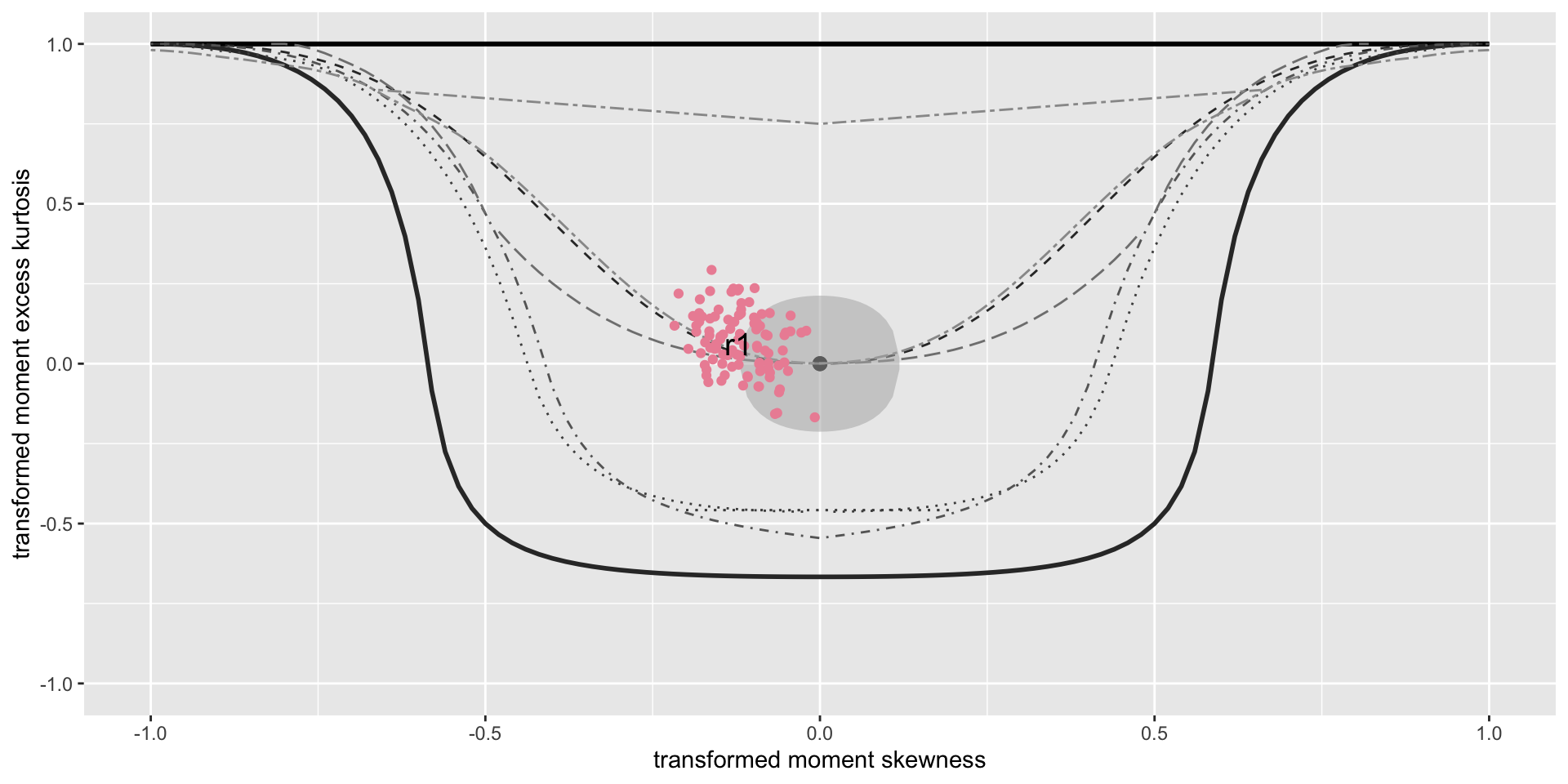
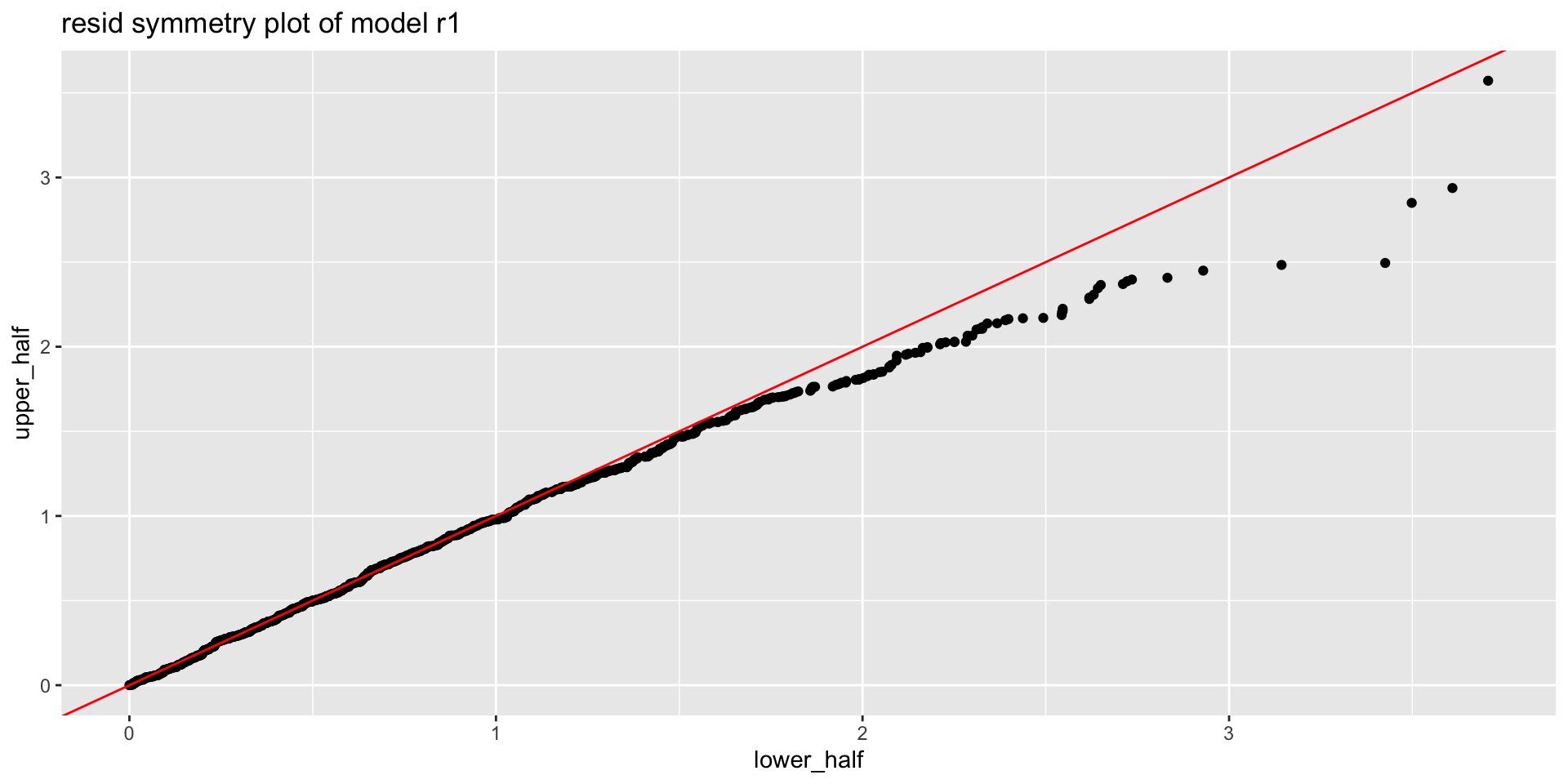
symmetry plots
ecdf plot

detrended ecdf plot
all in one plots
all in one plots (standard)

R-packages
Older Packages
gamlss: the original (needsdistanddata)gamlss.dist: defining thegamlss.familydistributionsgamlss.data: for extra data setsgamlss.add: connect withmgcv,nnetandtreesgamlss.tr: for truncatinggamlss.familydistributionsgamlss.cens: for censored response variablesgamlss.demo: for demonstrating GAMLSS conceptsgamlss.mx: for fitting finite mixtures
New Packages
gamboostLSSfor GAMLSS boostingbamlssthe Bayesian GAMLSSgamlss2\(^*\): the new version of GAMLSSgamlss.ggplots: usingggplot2within GAMLSSgamlss.foreach: for parallel computinggamlss.prepdata: preparation of data before fittinggamlss.lasso: for LASSO. Ridge and elastic Net regressiongamlss.shiny\(^*\): similar togamlss.demotopmodelsdistributional regression help (not necessary gamlss)
why gamlss2
gamlss()for very large data is slowpredictingamlssis not easy to usecurrent implementation can cope with only 4 parameters \(\mu\), \(\sigma\), \(\nu\) and \(\tau\)
to connect different estimation statistical approaches
penalised likelihoodBayesianboosting
to implement extra algorithms i.e.
stepwise,robustto implement
machine learningmethodology
getting the libraries
- For
CRANuseinstall.packages(gamlss)
- for
GitHubusedevtools::install_github("gamlss-dev/gamlss2")- https://gamlss-dev.r-universe.dev/builds
- and then use
library(gamlss2)
Practical 1
end


 The Books
The Books

www.gamlss.com