Centile estimation
Introduction
The data
the problem
the methods
the LMS and GAMLSS
the procedure
the data
The Dutch boys data Source: Buuren and Fredriks (2001)
head: the head head circumference of 7040 boysage: the age in years
the data plot
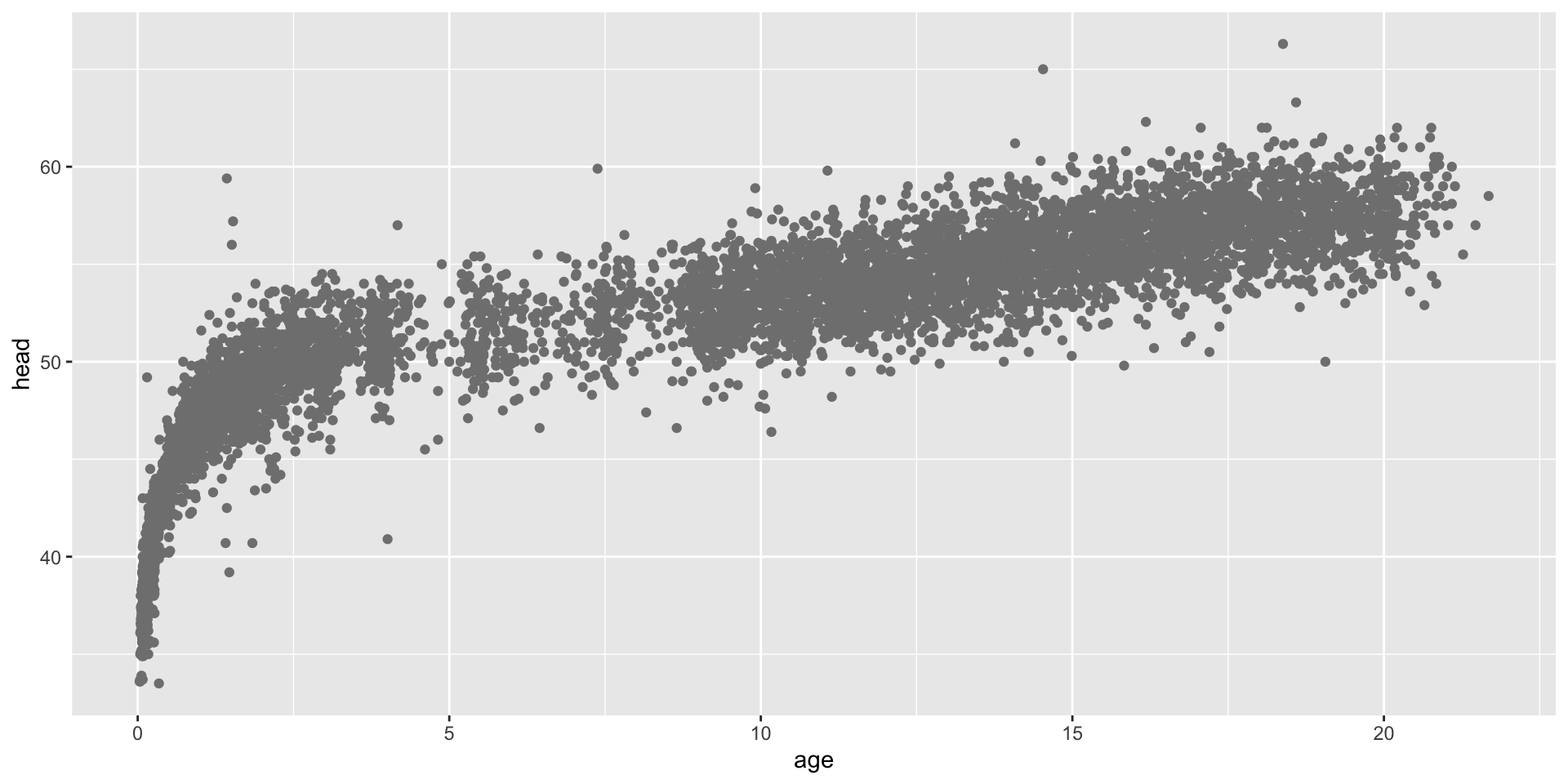
estimate the curves
the target
the methods
the non parametric approach of
quantile regression(Koenker, 2005; Koenker and Bassett, 1978)the parametric
LMSapproach of Cole (1988), Cole and Green (1992) and its extensions Rigby and Stasinopoulos (2004, 2006, 2007).
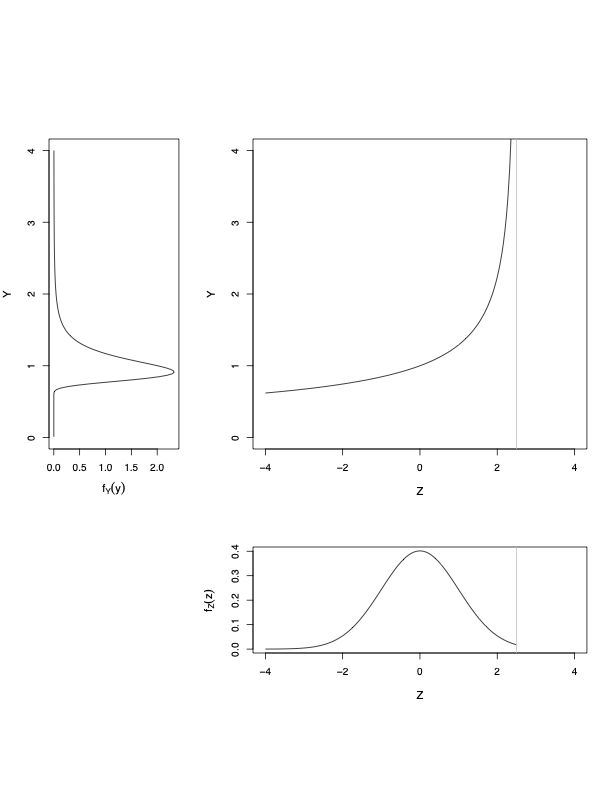
the LMS method
\[Y \sim f_Y(y| \mu, \sigma, \nu, \tau )\] where \(f_Y()\) is theoretical distribution,
- \(y\) =
head circumferenceand
- \(x\) =
age\(^\xi\) - \(\mu\) = s(x, \(df_\mu\))
- \(\sigma\) = s(x, \(df_\sigma\))
- \(\nu\) = s(x, \(df_\nu\))
- \(\tau\) = s(x, \(df_\tau\))
the LMS method
\(y\) is defined through \(z\)
\[\begin{eqnarray} z = \frac{1}{\sigma \nu} \left[\left( \frac{y}{\mu}\right)^{\nu}-1 \right], & \ \textrm{if} \ \nu \neq 0 \nonumber \\ = \frac{1}{\sigma}\log\left(\frac{y}{\mu}\right), & \ \textrm{if} \ \nu =0. \nonumber \end{eqnarray}\]- if \(Z \sim N(0,1)\) then \(Y \sim BCCG(\mu, \sigma, \nu) =\)
LMSmethod
LMS extentions
if \(Z \sim N(0,1)\) then \(Y \sim BCCG(\mu, \sigma, \nu) =\)
LMSmethodif \(Z \sim t_{\tau}\) then \(Y \sim BCT(\mu, \sigma, \nu, \tau)=\)
LMSTmethodif \(Z \sim PE(0,1,\tau)\) then \(Y \sim BCPE(\mu, \sigma, \nu, \tau)=\)
LMSPmethod adopted by WHO}
Box-Cox & Cole-Green transformation
estimation of smoothing parameters
by trial and error
minimize the generalized Akaike information criterion, GAIC()
minimize the the validation global deviance VGD
using local selection criteria, i.e. CV, ML
procedure
select the transformation parameter \(\xi\)
fit different model and choose the minimim GAIC()
use diagnostic tools
get the centiles
transformation parameter \(\xi\)
library(gamlss2)
library(gamlss.ggplots)
gamlss.ggplots:::find_power(y=db$head, x=db$age, profile=TRUE, from=0, to=1, step=0.01)*** Checking for transformation for x *** *** power parameters 0.24 *** [1] 0.24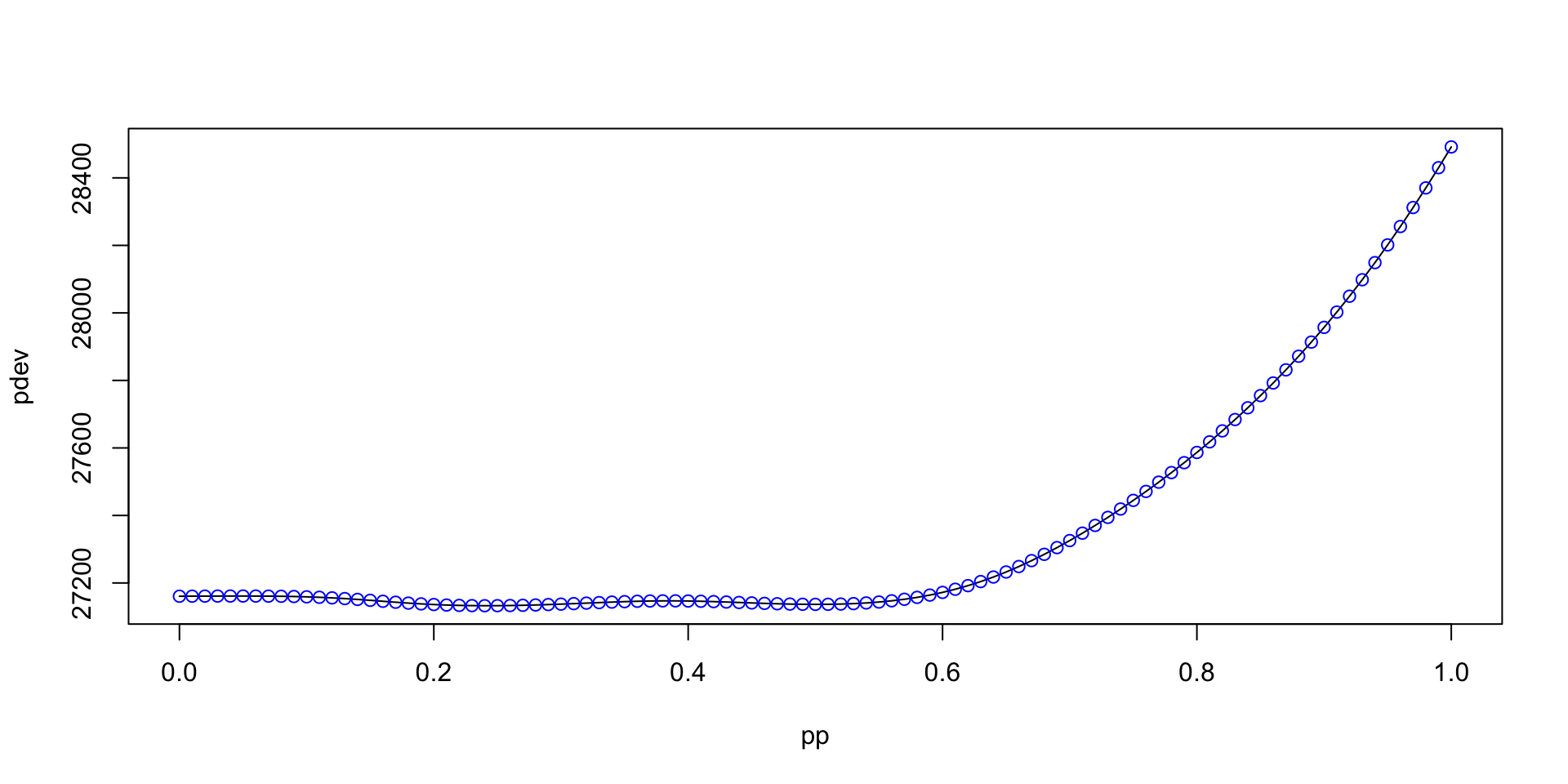
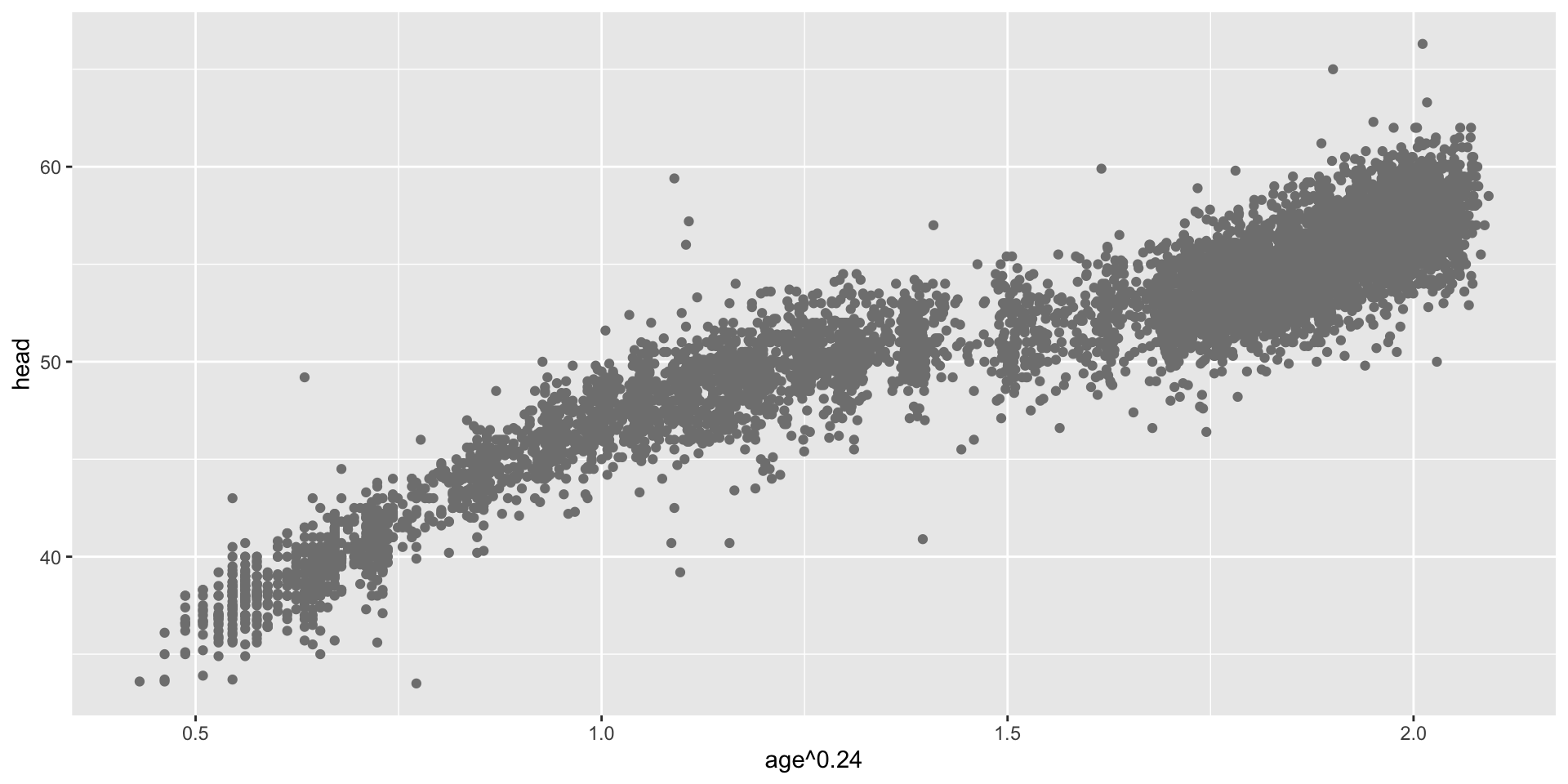
transformation parameter \(\xi\) (con.)
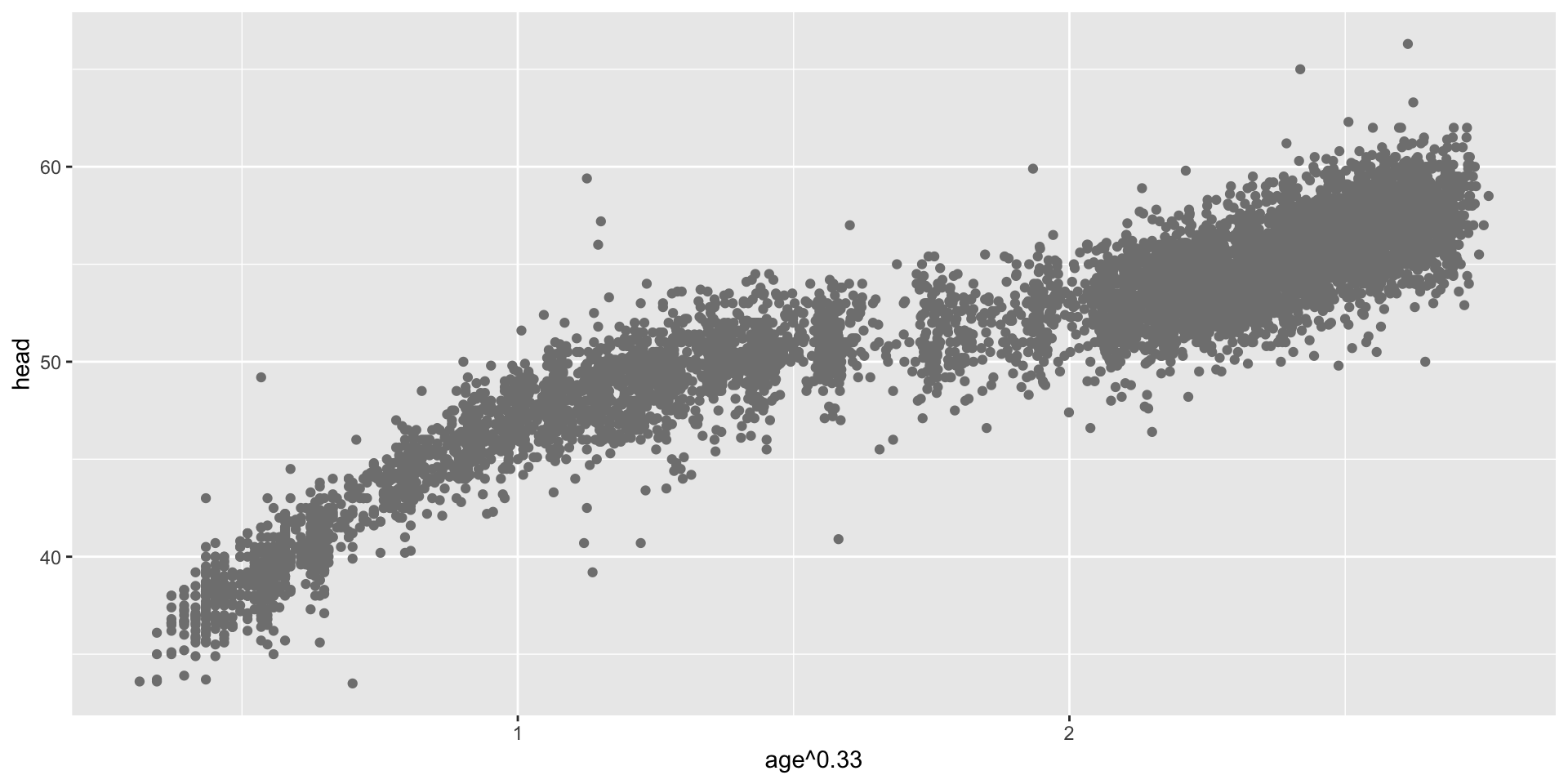
transformation parameter \(\xi\) (con.)
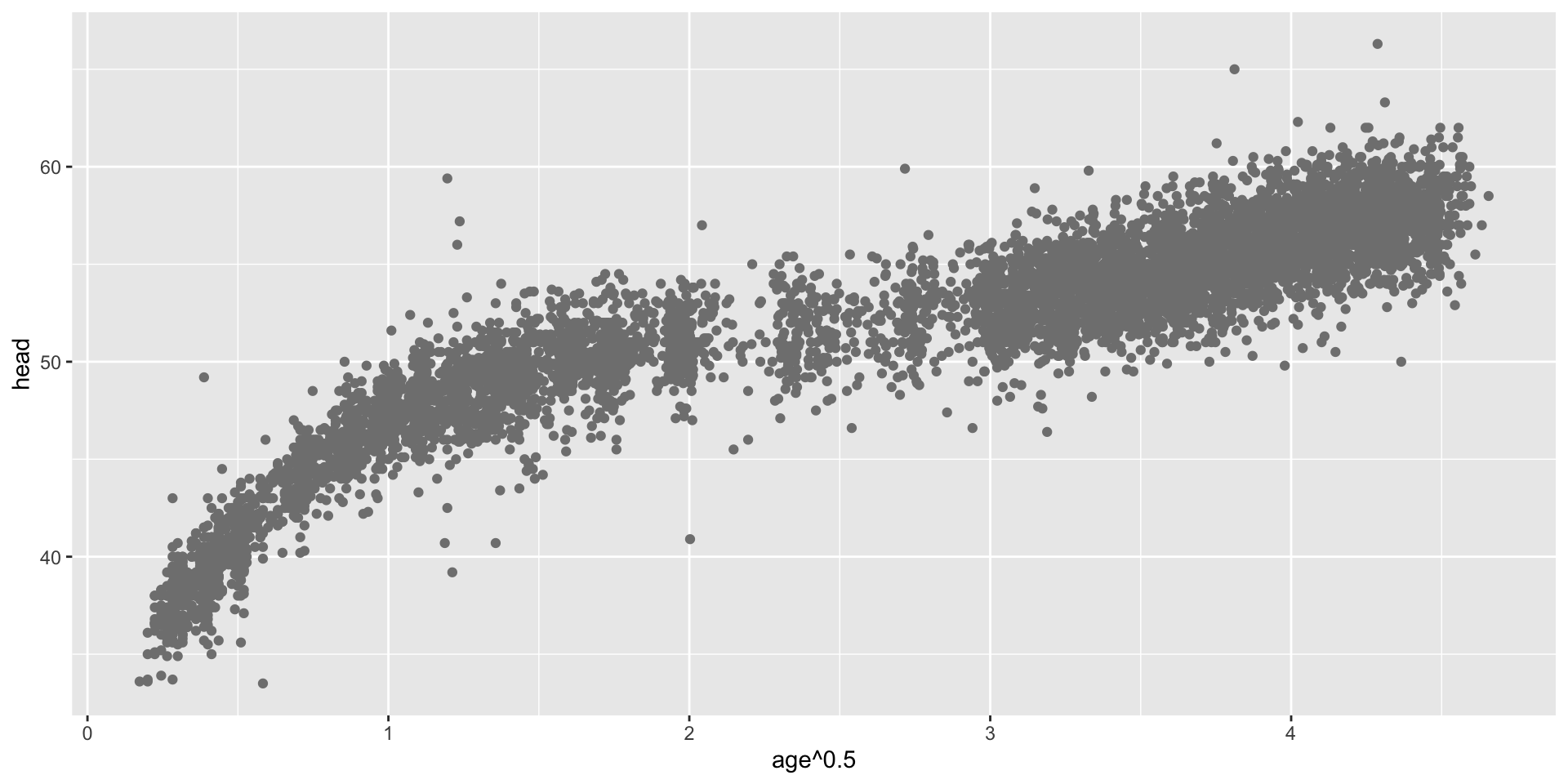
transformation parameter \(\xi\) (con.)
transformation parameter \(\xi\) (summary.)
smoothing techniques can not cope with sudden changes
if the sudden change is in the end of the data transforming using \(\xi\) could help
if the sudden change is in the middle a different transormation is required
alternatively using adapting smoothing parameter can help
fit different models
GAMLSS-RS iteration 1: Global Deviance = 27047.653 eps = 0.384661
GAMLSS-RS iteration 2: Global Deviance = 27005.107 eps = 0.001573
GAMLSS-RS iteration 3: Global Deviance = 27005.0941 eps = 0.000000 GAMLSS-RS iteration 1: Global Deviance = 27134.2939 eps = 0.389668
GAMLSS-RS iteration 2: Global Deviance = 26944.0924 eps = 0.007009
GAMLSS-RS iteration 3: Global Deviance = 26941.8838 eps = 0.000081
GAMLSS-RS iteration 4: Global Deviance = 26941.8334 eps = 0.000001 gBCPEo <- gamlss2(head~s(I(age^.33))|s(I(age^.33))|s(I(age^.33))|s(I(age^.33)), data=db, family=BCPEo)GAMLSS-RS iteration 1: Global Deviance = 27412.103 eps = 0.377203
GAMLSS-RS iteration 2: Global Deviance = 26825.7069 eps = 0.021391
GAMLSS-RS iteration 3: Global Deviance = 26822.0093 eps = 0.000137
GAMLSS-RS iteration 4: Global Deviance = 26821.9891 eps = 0.000000 gBCTo <- gamlss2(head~s(I(age^.33))|s(I(age^.33))|s(I(age^.33))|s(I(age^.33)), data=db, family=BCTo)GAMLSS-RS iteration 1: Global Deviance = 26940.9697 eps = 0.390731
GAMLSS-RS iteration 2: Global Deviance = 26749.7364 eps = 0.007098
GAMLSS-RS iteration 3: Global Deviance = 26747.984 eps = 0.000065
GAMLSS-RS iteration 4: Global Deviance = 26747.8873 eps = 0.000003 select models
AIC df
gBCTo 26792.07 22.08936
gBCPEo 26871.06 24.53565
gBCCGo 26998.12 28.14446
gNO 27042.92 18.91385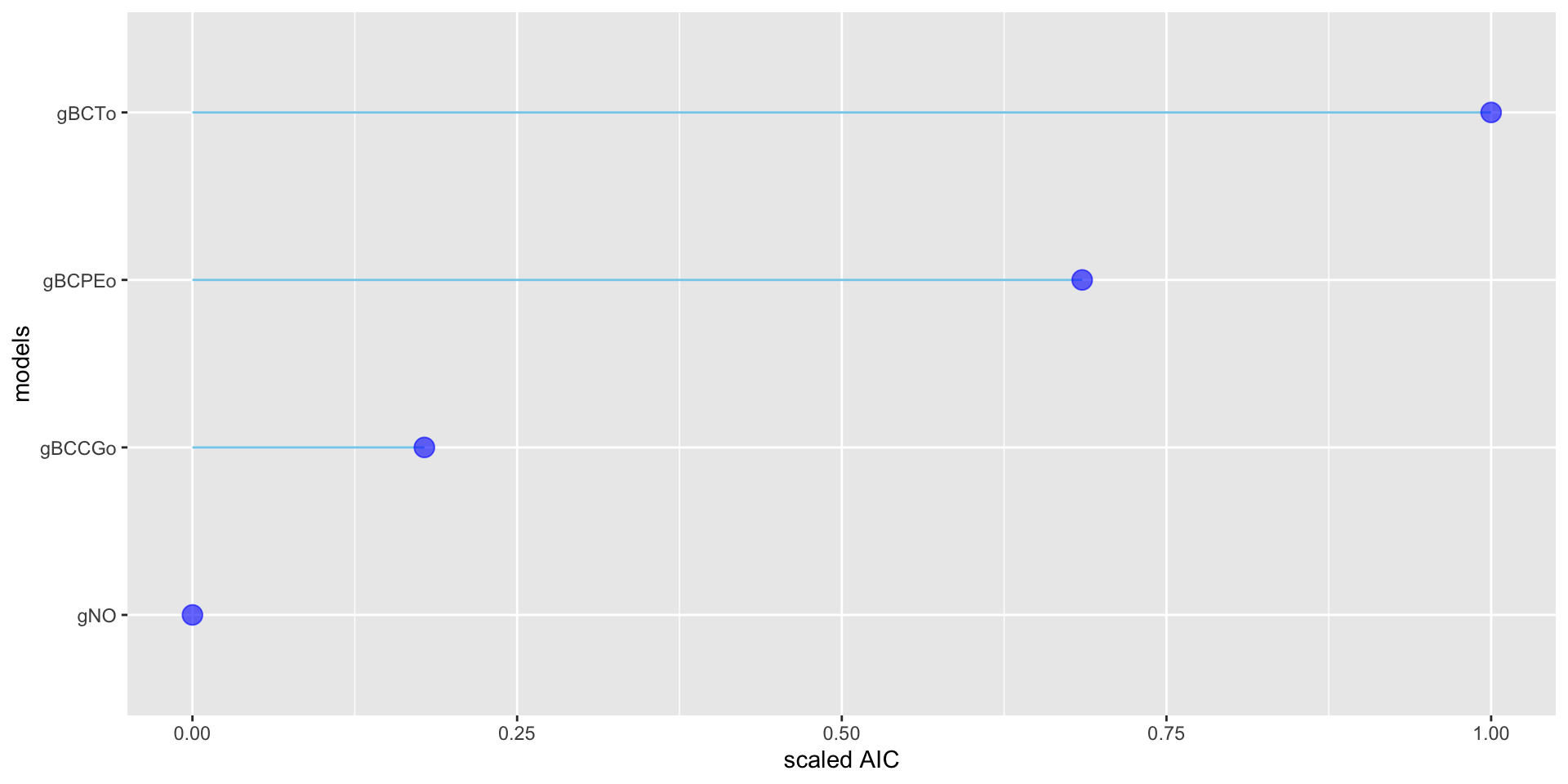
diagnostic tools: residuals
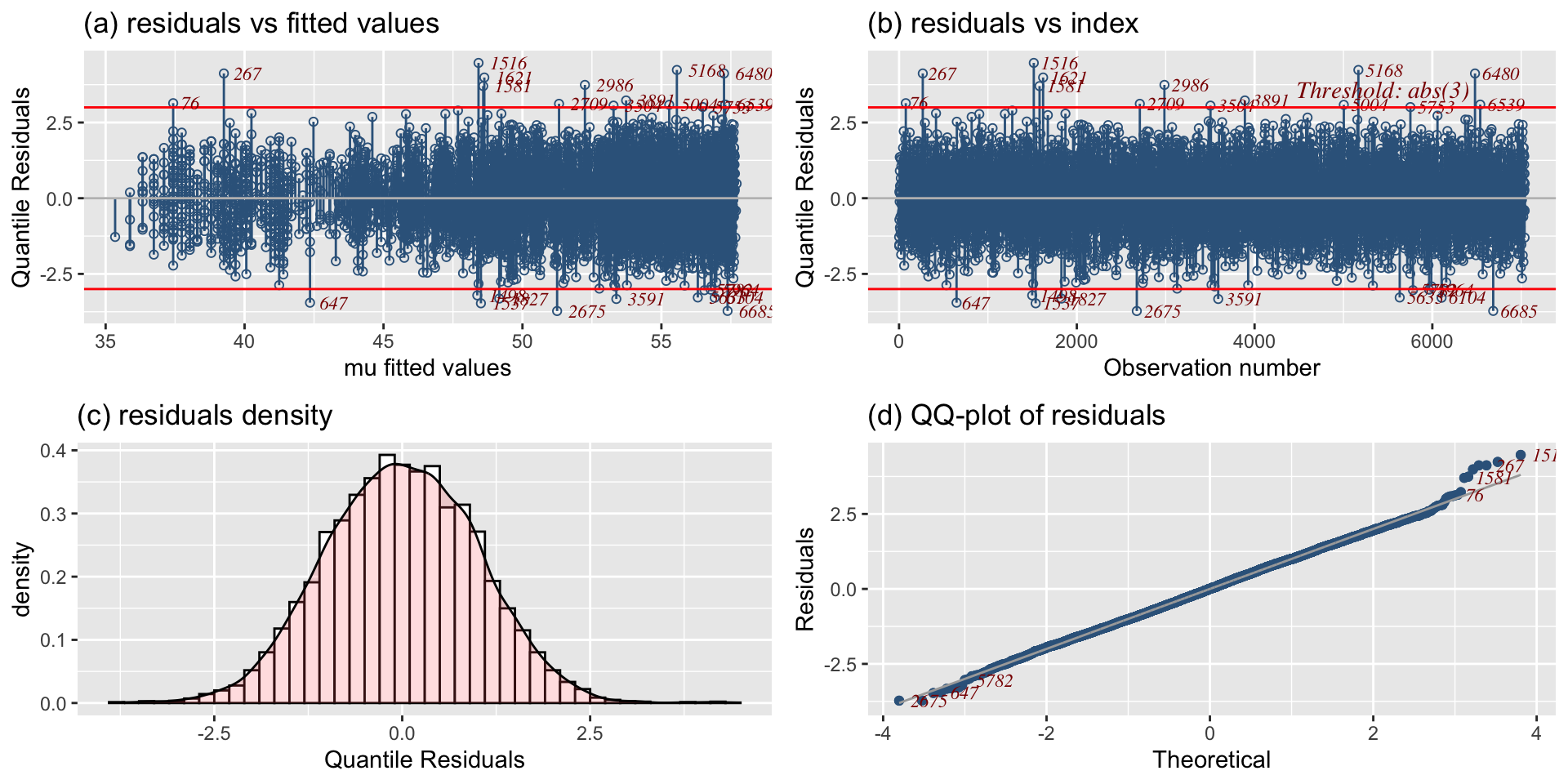
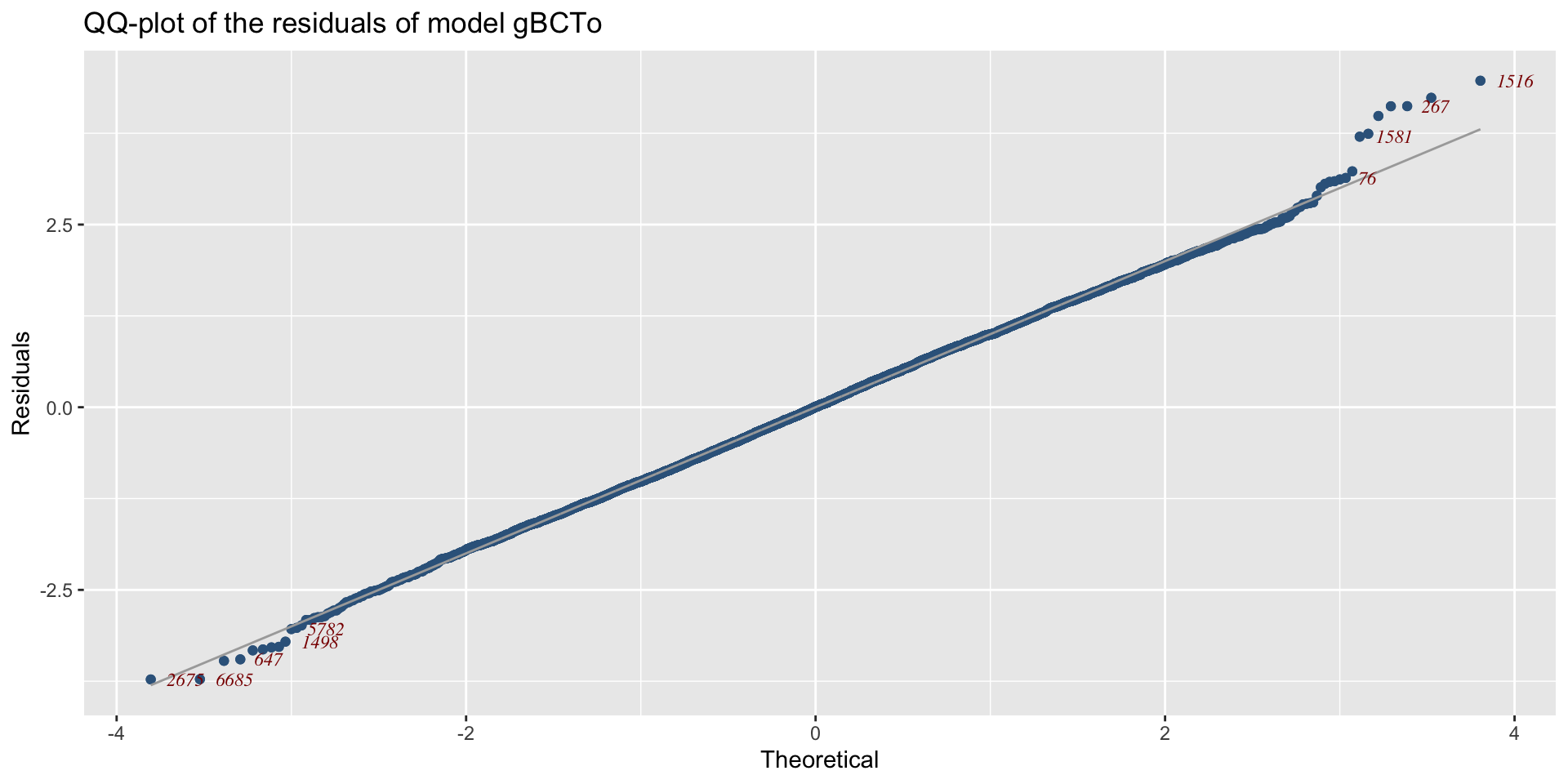
QQplot
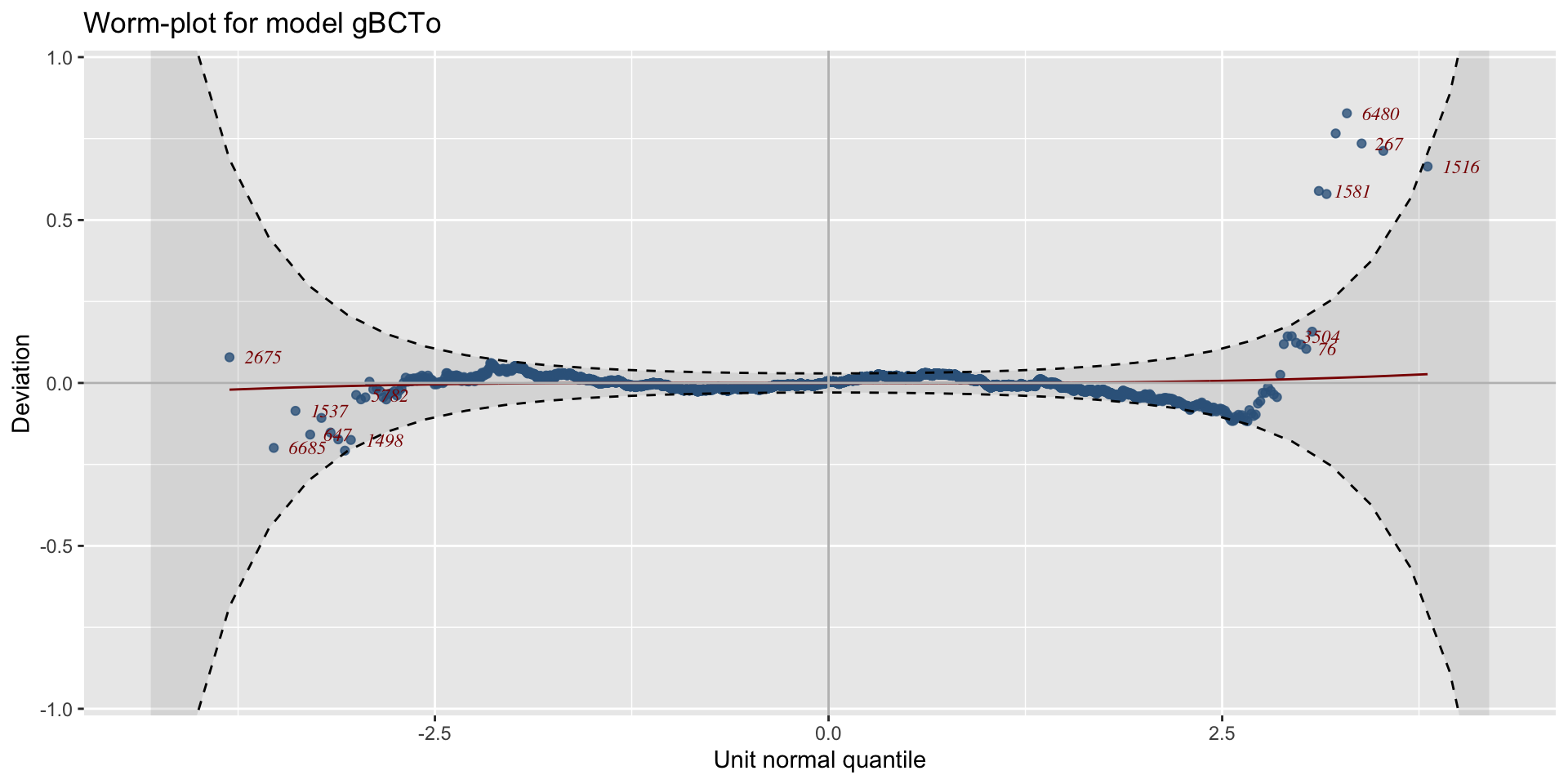
worm plots
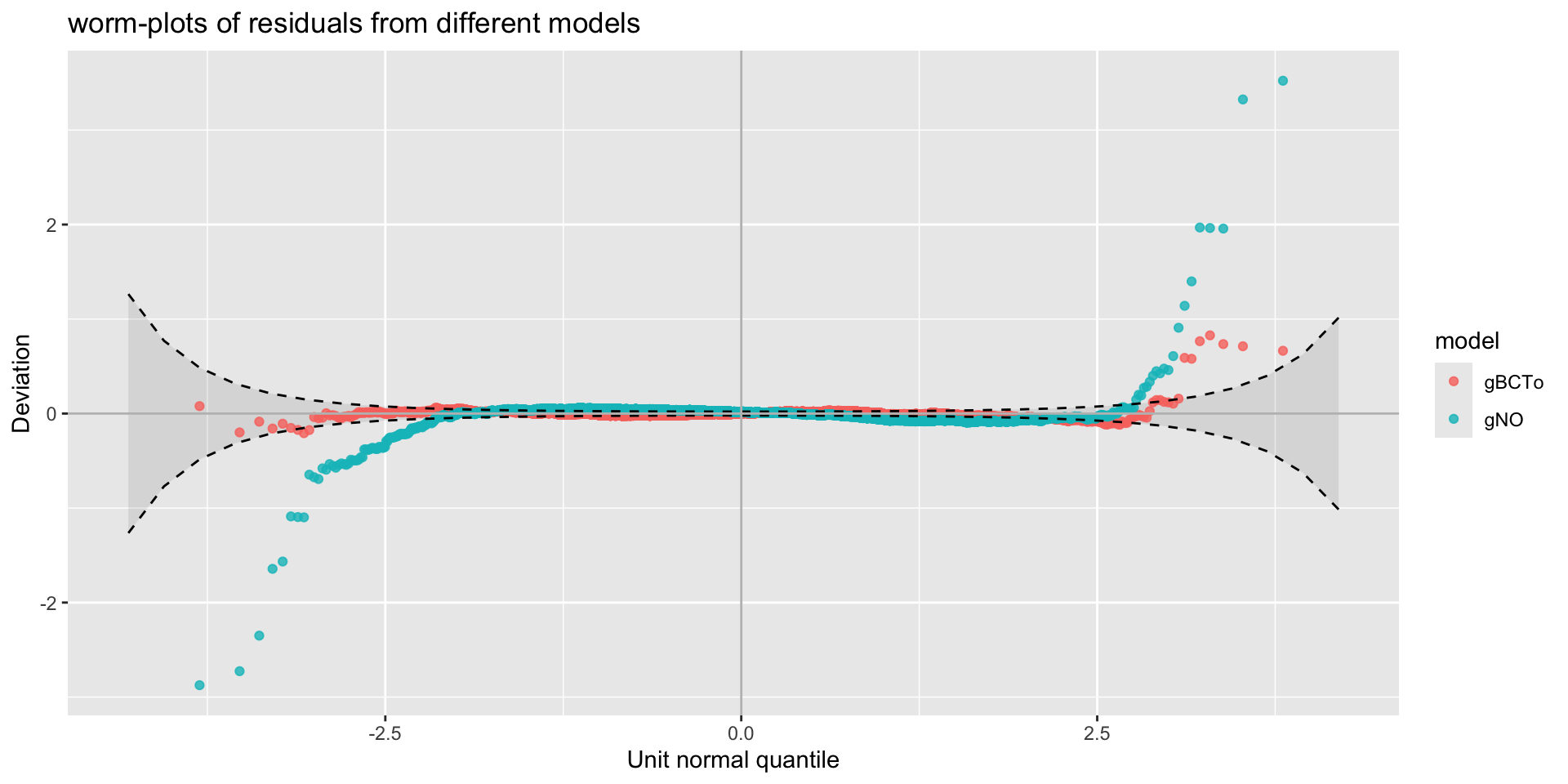
different models worm plots
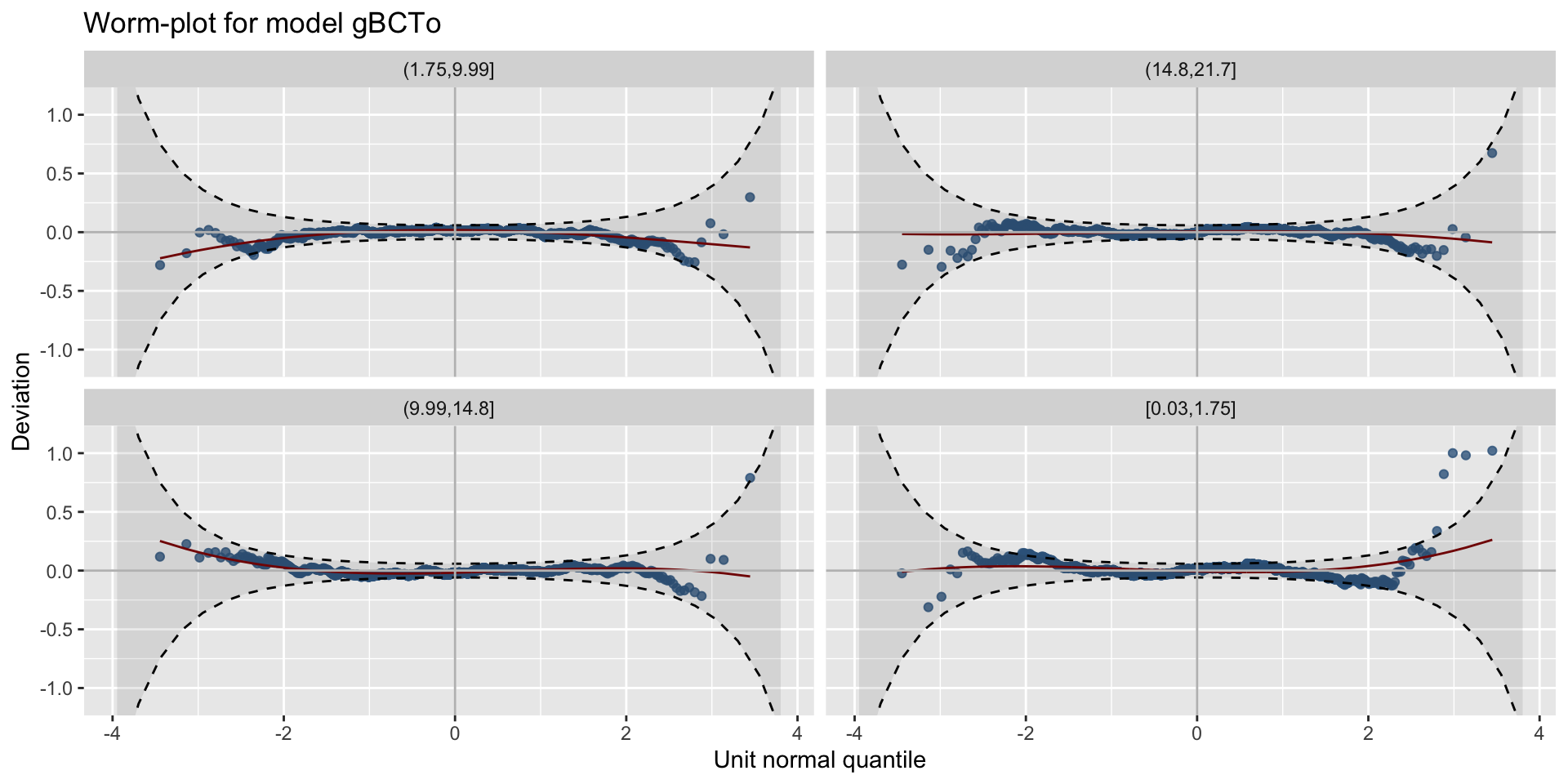
different x-values worm plots
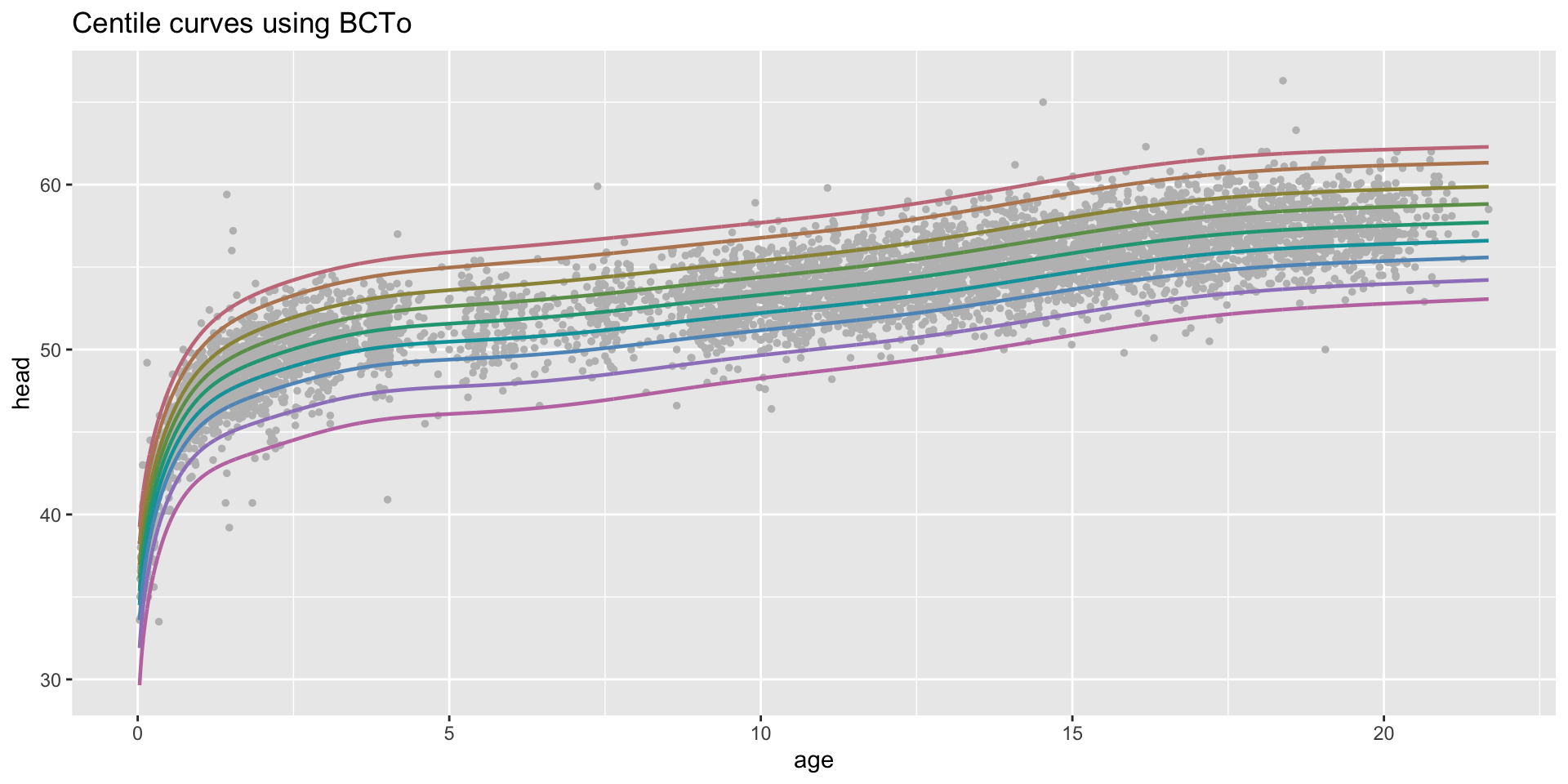
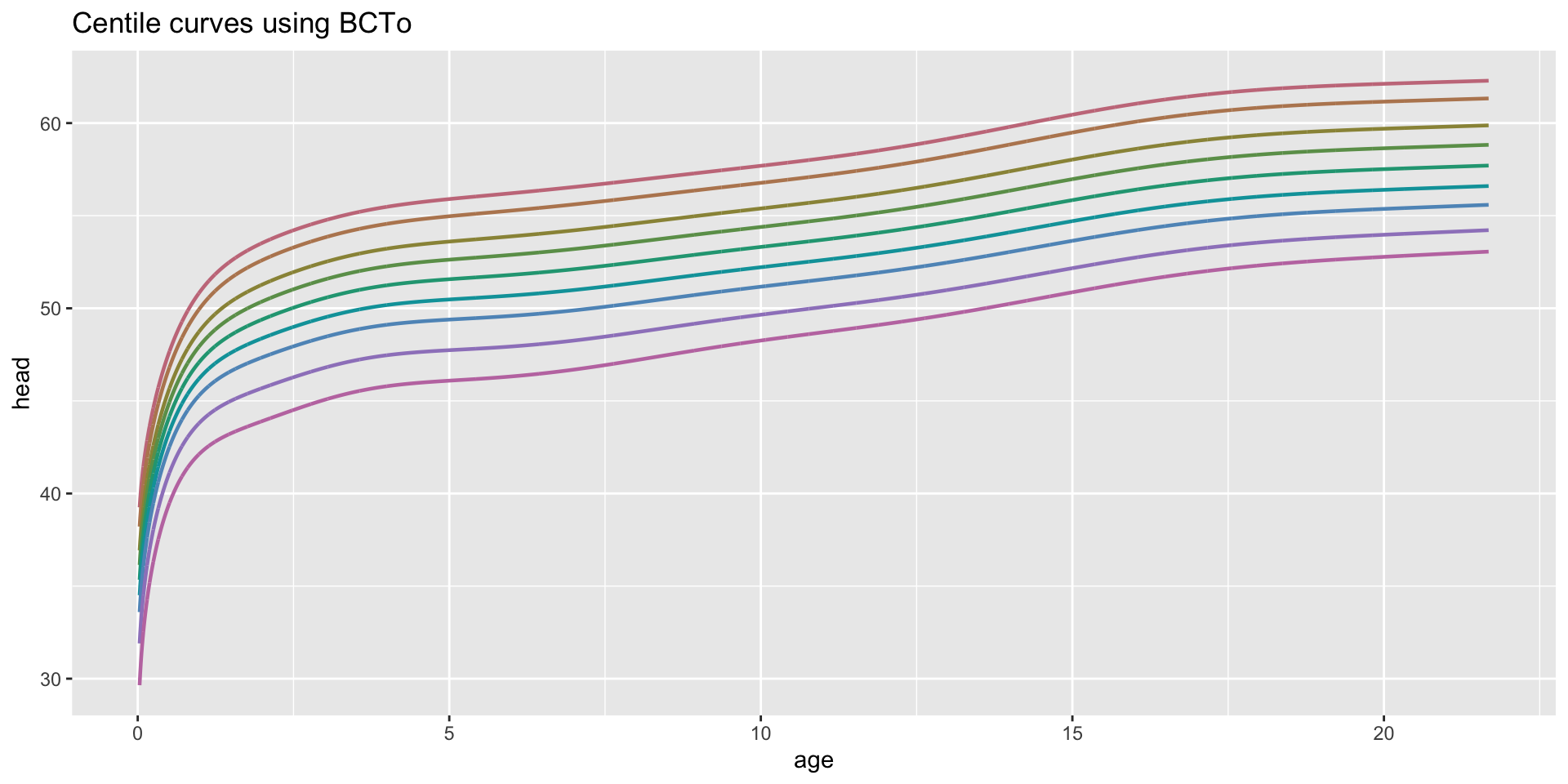
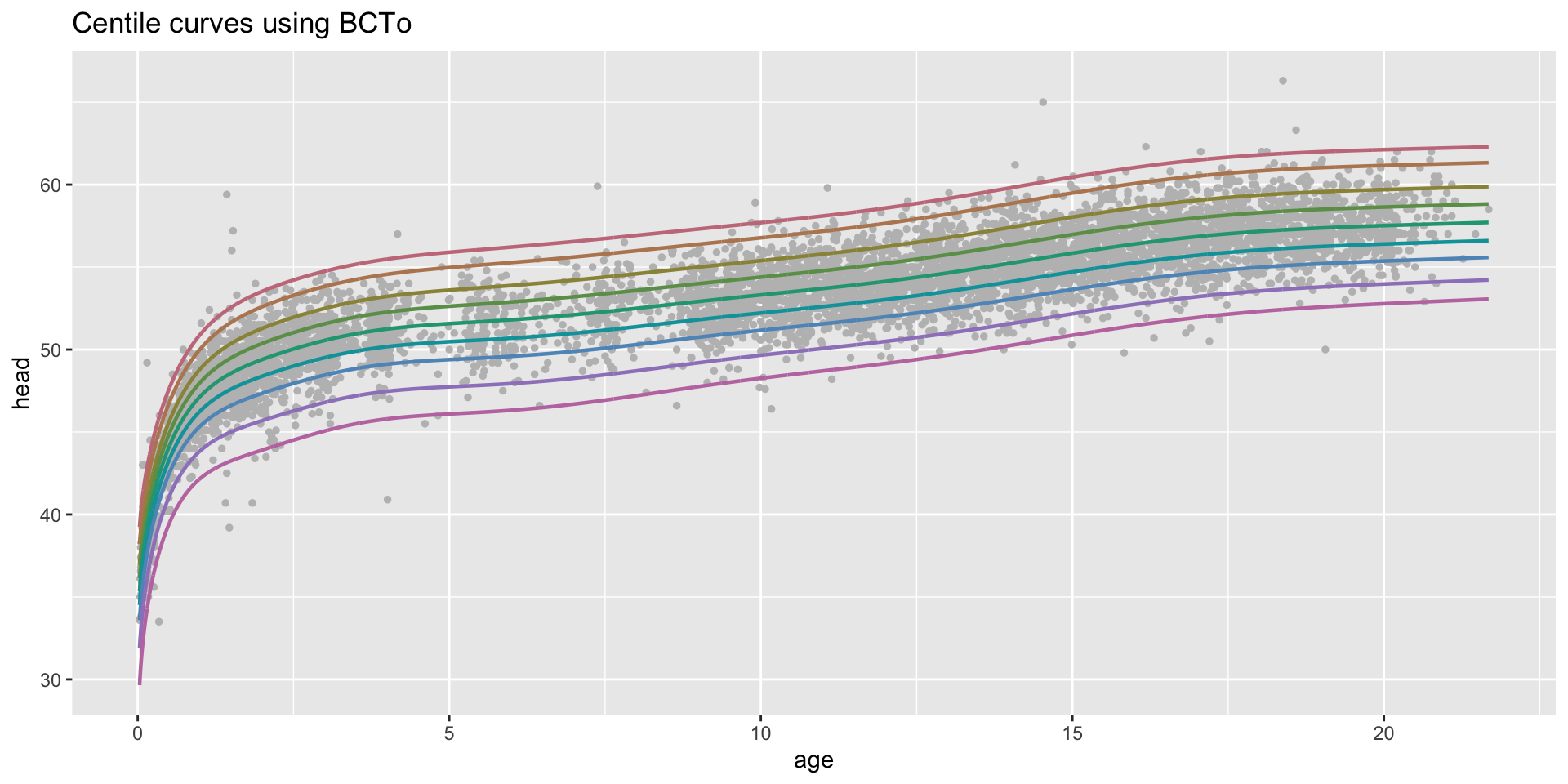
centiles
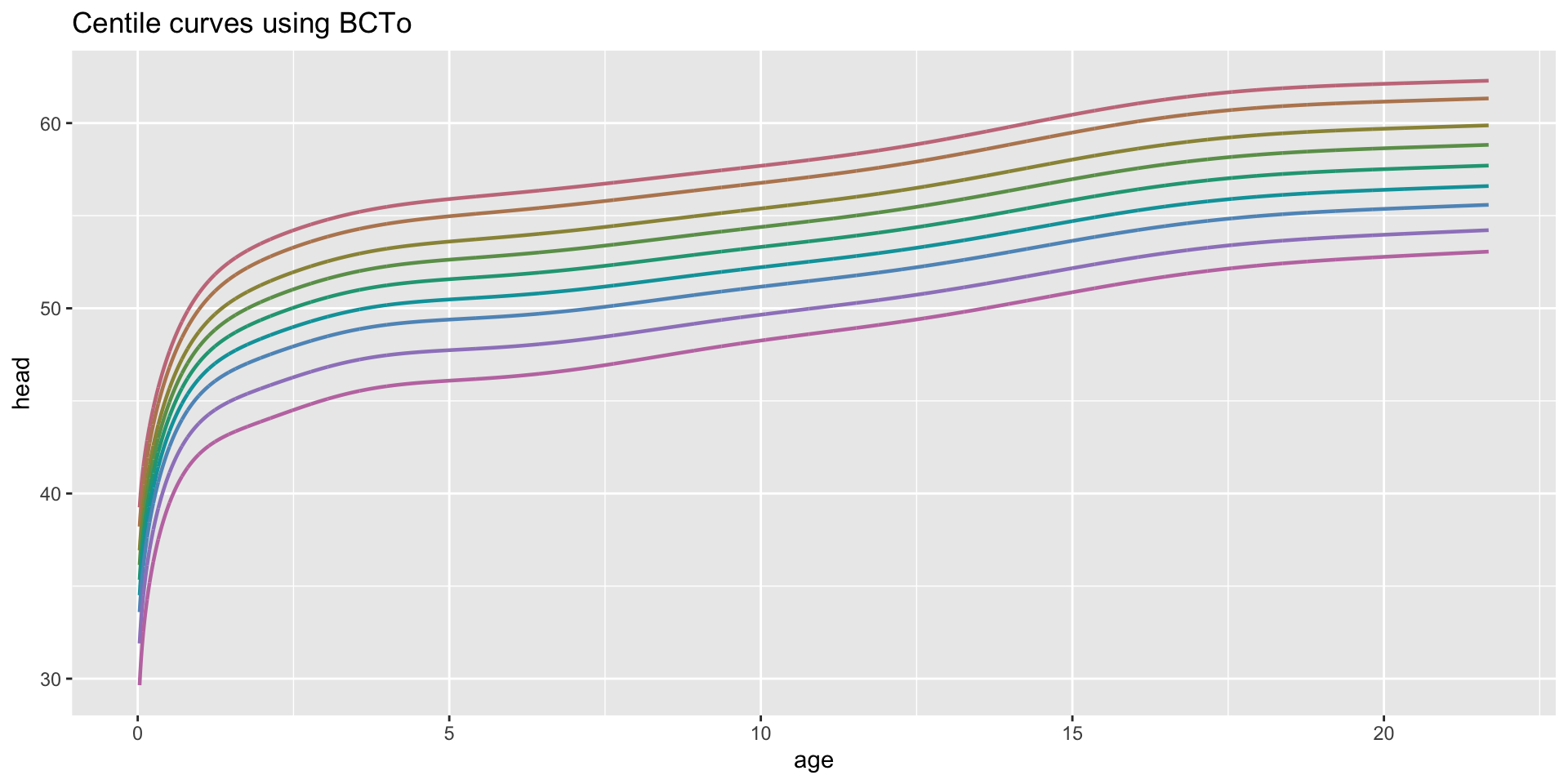
centiles just curves
centiles with legend
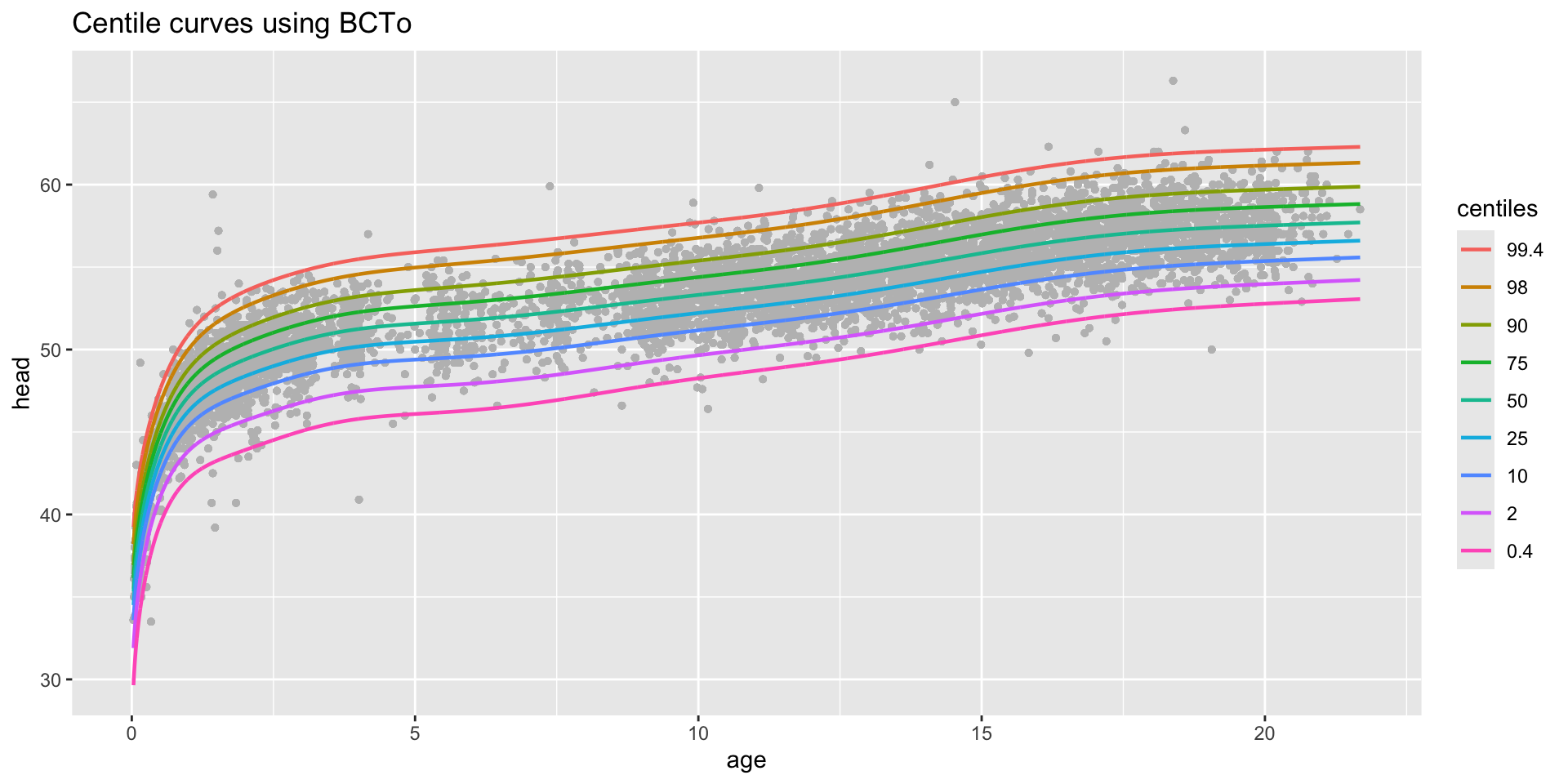
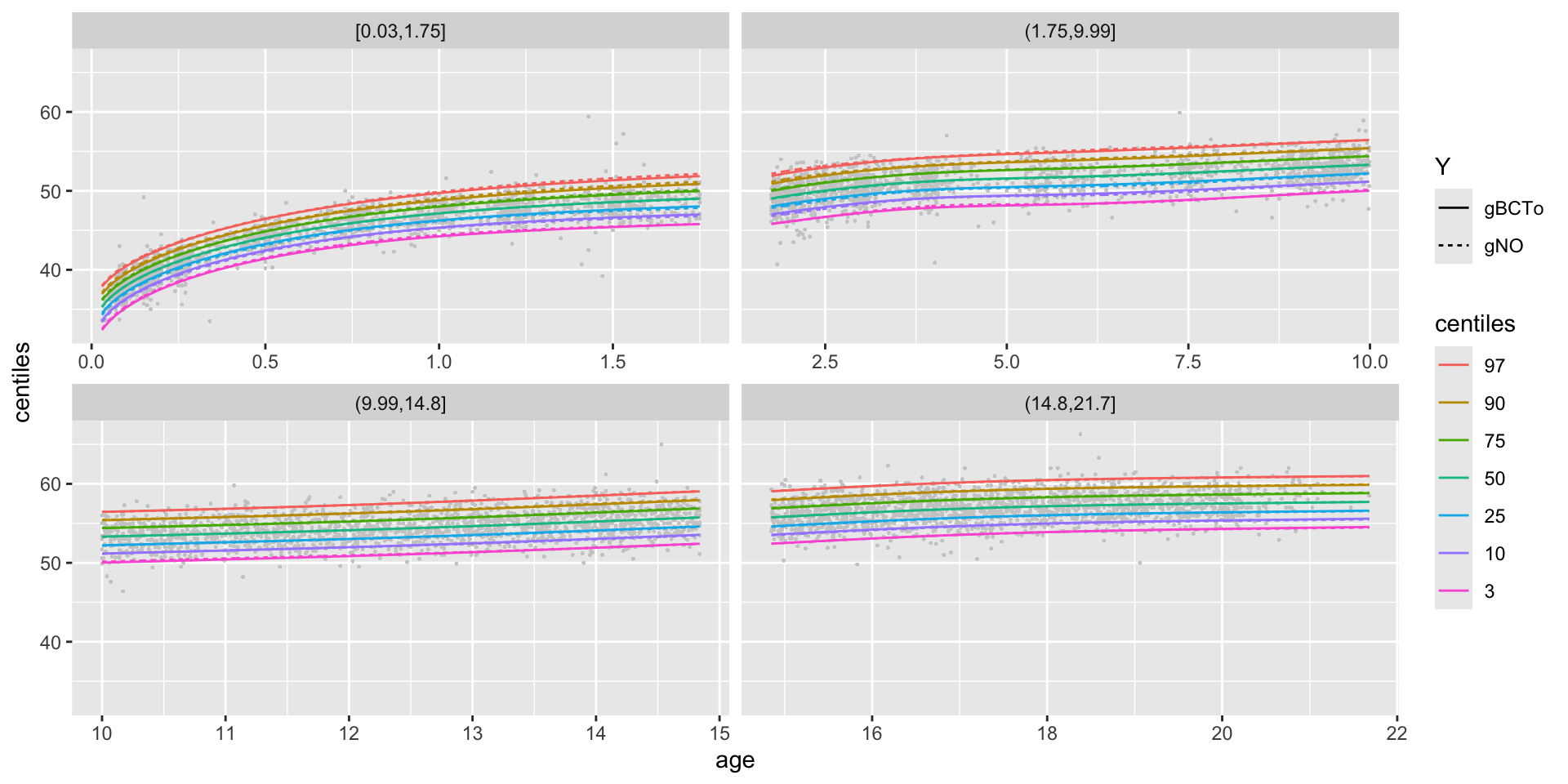
centiles different models
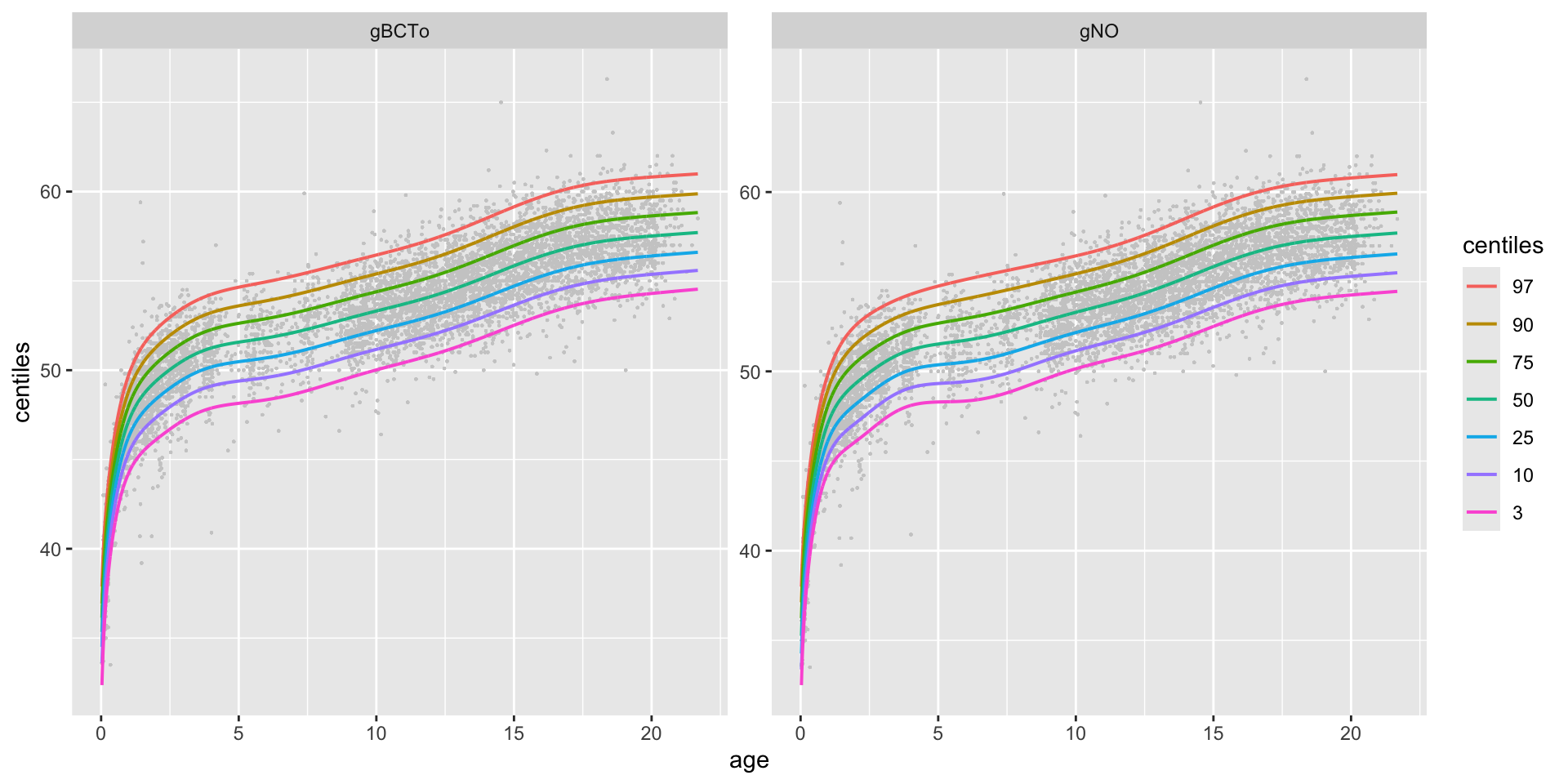
centiles different models in one plot
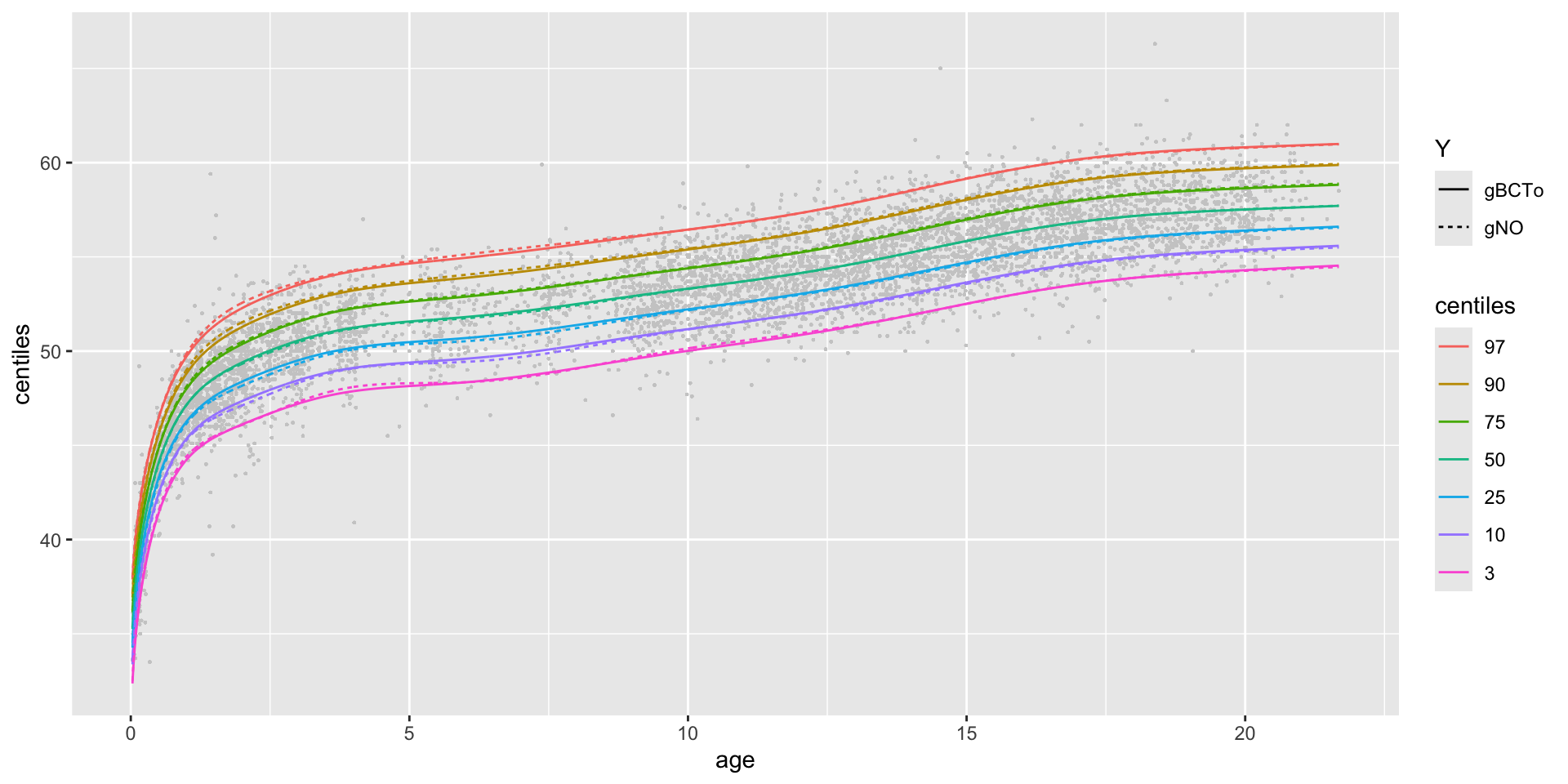
centiles different models in one plot
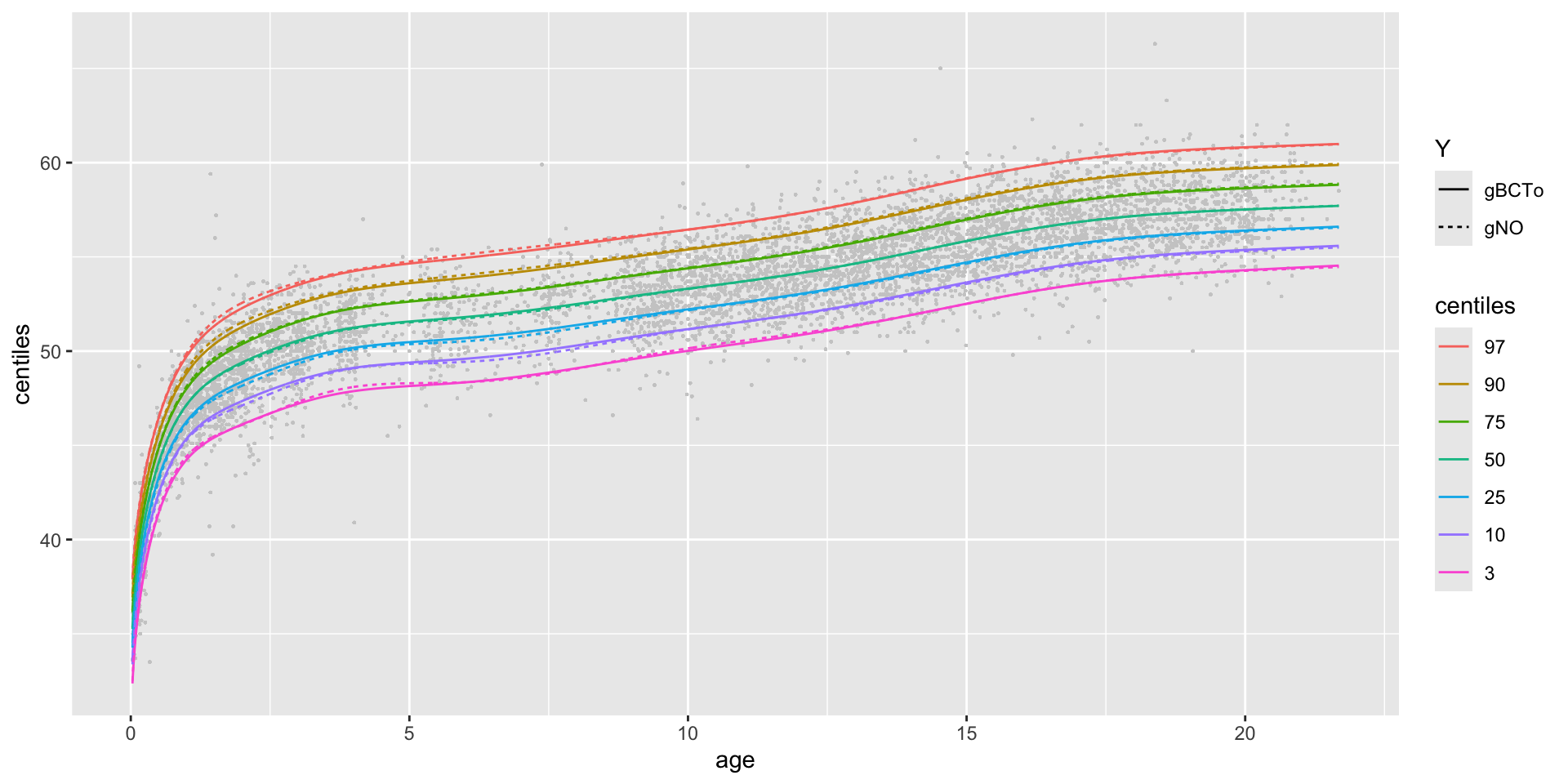
centiles different models different x-valus in one plot
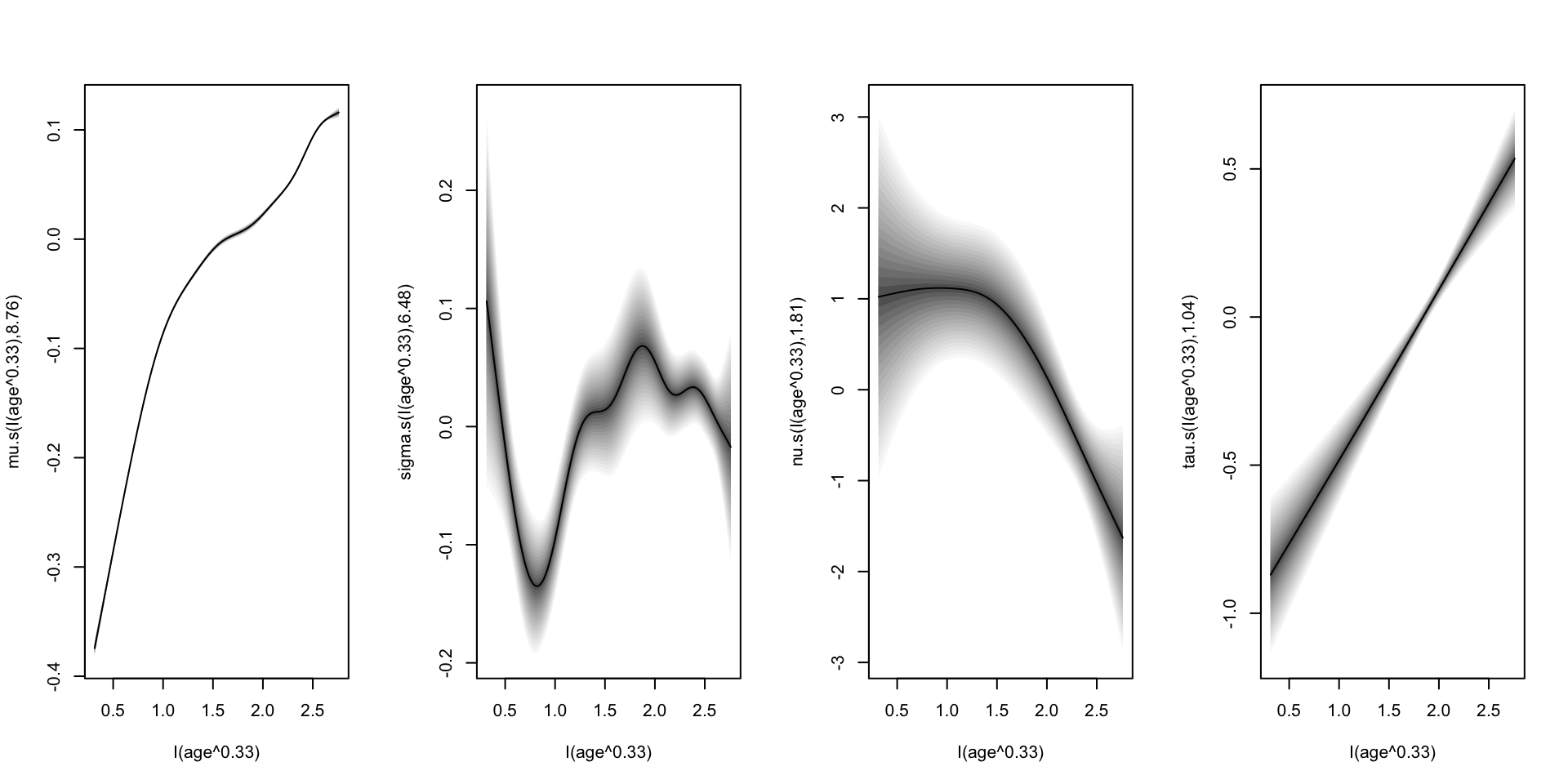
fitted parameters
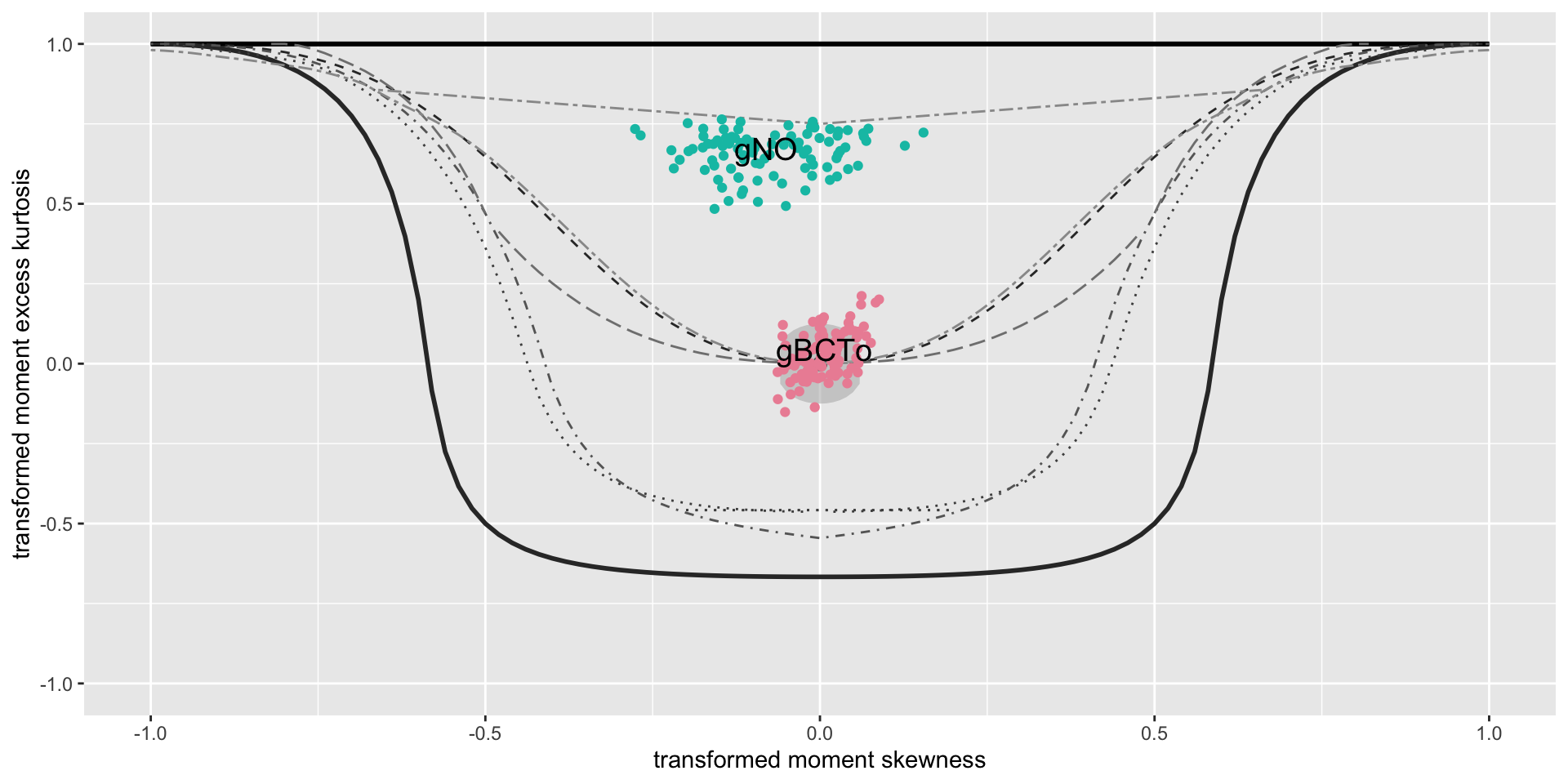
bucket plots
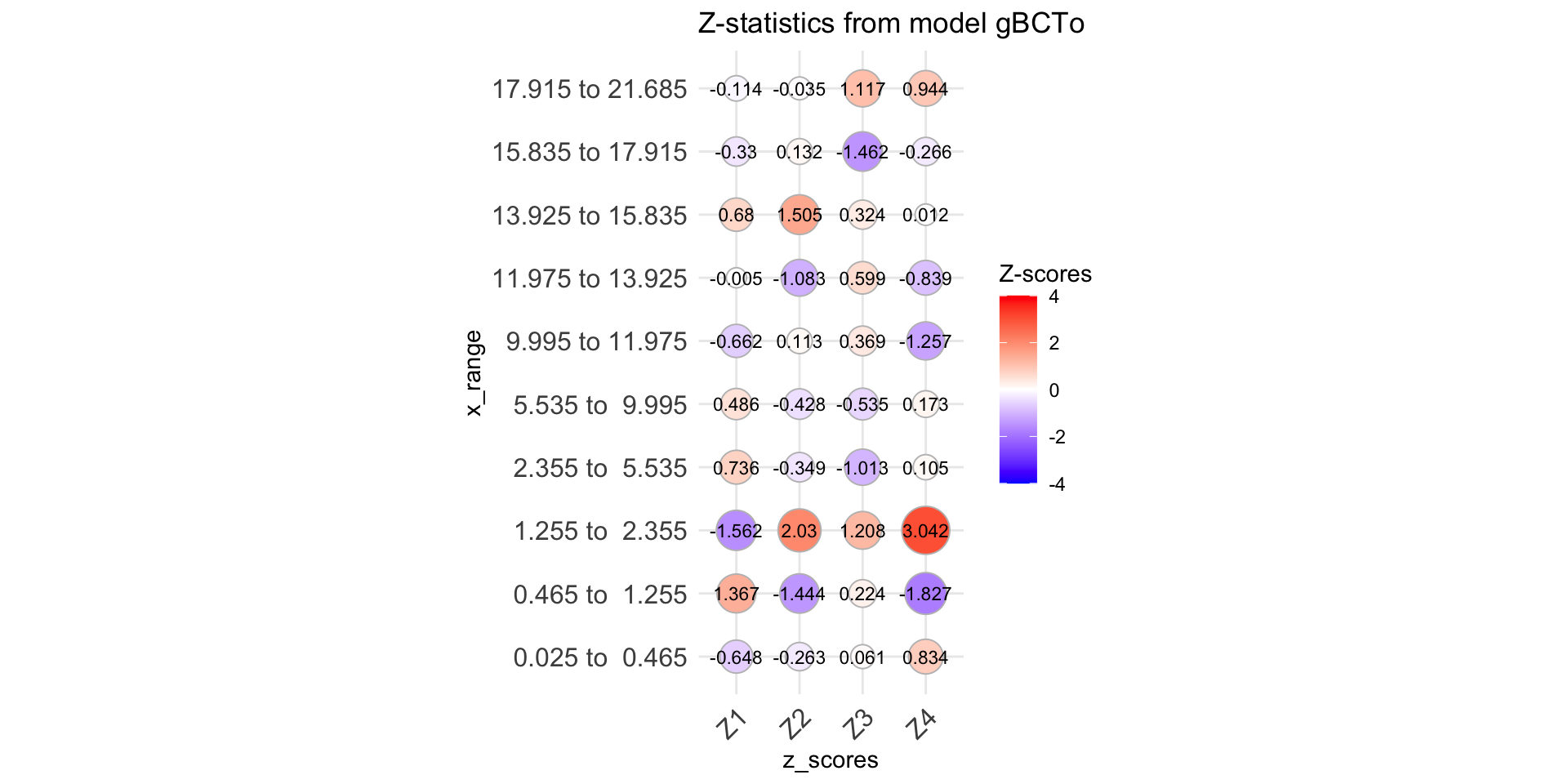
Q-stats
predict
library(broom)
library(knitr)
da <- predict(gBCTo, newdata=db[c(1, 1000, 2000, 3000, 6000,7000),])
da |> head() |> kable(digits = c(2, 4, 4, 4), format="pipe")| mu | sigma | nu | tau | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35.34 | 0.0317 | 3.0297 | 4.8899 |
| 1042 | 46.10 | 0.0253 | 3.1266 | 6.8850 |
| 2091 | 49.50 | 0.0286 | 3.0847 | 8.3999 |
| 3118 | 52.27 | 0.0304 | 2.2706 | 12.3616 |
| 6327 | 56.82 | 0.0290 | 0.8780 | 17.5648 |
| 7422 | 57.57 | 0.0283 | 0.4968 | 19.3337 |
end


 The Books
The Books

www.gamlss.com